Skin melanoma
Machine translation
Original article is written in RU language (link to read it).
Melanoma is a malignant neoplasm, the source of which is melanocytes. As a rule, this tumor has a black or brown color, which is due to the production of melanin by melanocytes.
Melanoma is a relatively rare tumor compared to other forms of cancer, but it is a very serious disease. The localization of melanoma can be completely different, on any area of the skin; the darker a person’s skin, the lower the likelihood of developing melanoma. Cases of melanoma being detected under the nails, on the soles and palms of patients have been recorded.
More useful and relevant information, including on malignant neoplasms, in the section of our website Training in maxillofacial surgery .
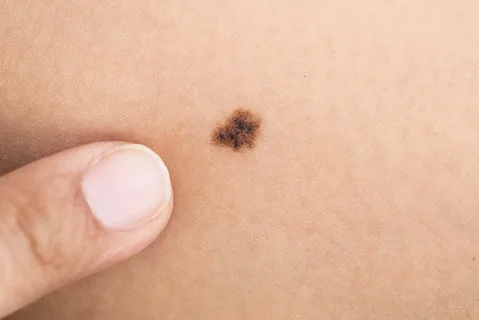
Figure 1. Melanoma.
Risk factors
The risk of developing melanoma increases if the patient has the following factors:
Nevi are benign melanotic neoplasms that are not present at birth, but appear by adolescence. Certain types of nevi contribute to the formation of melanoma.
Atypical moles, dysplastic nevi, more often cause the development of melanoma. They are localized on areas of the skin unprotected from sunlight, and sometimes on hidden areas. These nevi are large, their size exceeds the size of a typical mole. Sometimes multiple dysplastic nevi occur; as a rule, this is a hereditary disease.
Non-dysplastic nevi, non-hereditary nevi, extremely rarely degenerate into melanoma. People who have numerous moles, or some large ones, have a higher risk of developing melanoma.
Blonde hair, fair skin, freckles. People with fair skin are 20 times more likely to develop melanoma compared to African Americans. This circumstance is due to the protective effect of skin pigment. White people with blond or red hair, which is often covered with freckles, are easily sunburned, which significantly increases the risk of melanoma.
Heredity. If one of the patient's close relatives suffered from melanoma, this significantly increases the risk of developing melanoma.
Immunosuppression. People who have undergone organ transplantation and are therefore forced to take medications that suppress the immune system throughout their lives have a higher risk of developing neoplasms, including melanoma.
Abuse of tanning, excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation, the main source of which is solar radiation, lamps and solarium booths. Individuals overexposed to these sources of ultraviolet radiation have a significantly increased risk of melanoma. Excess UV exposure is determined by the intensity of the light, the duration of exposure, and the presence of protective shields and clothing. If you have a history of severe sunburn of the skin with blisters, the risk of a malignant neoplasm on the skin increases sharply.
Age. Melanoma predominantly occurs among patients over 50 years of age. At the same time, melanoma is the most common tumor among young people under 30 years of age.
Floor. According to long-term statistics, males are susceptible to developing melanoma much more often than females. However, the same statistical analysis showed that in recent decades the number of cases of melanoma among females has increased.
Xeroderma pigmentosum is a rare hereditary disease associated with the failure of an enzyme necessary to repair damaged DNA. Patients with xeroderma pigmentosum are characterized by an increased risk of malignant neoplasms of exposed skin areas exposed to frequent exposure to solar radiation.
History of melanoma. The insidiousness of this disease lies in the fact that a patient, once cured of melanoma, has a very high risk of its recurrence.

Figure 2. Nevi.
Although most nevi do not transform into melanoma, sometimes this still happens. Certain processes occurring in benign nevus cells can contribute to their transformation into melanoma cells. Until now, scientists have not been able to establish why some moles become malignant and others do not.
Prevention of melanoma
Being in the shade. The simplest, but extremely effective way to protect against excess ultraviolet radiation is to minimize the time spent in direct sunlight during lunchtime, when the influence of ultraviolet radiation is especially dangerous. It is important to take into account the fact that the sun's rays are reflected from snow, water, sand and cement.
Wearing protective clothing. Most of the surface of the skin can be hidden from the influence of sunlight through clothing made of dense, lightweight fabric and a hat that has a wide brim.
Applying sunscreen to the skin. Sunscreen is recommended to be used daily in the summer, when solar radiation is especially intense. It is important to consider that ultraviolet rays penetrate freely through fog and clouds. Lips also need to be covered with a protective agent. All these drugs do not prevent the development of melanoma, but only reduce the intensity of the influence of ultraviolet radiation.
Sunglasses can protect almost 100% of the eyes and surrounding skin from ultraviolet radiation.
Inspection and, if necessary, removal of nevi. The presence of certain types of nevi leads to an increased risk of melanoma. Excision of multiple moles is not recommended as a preventive measure for melanoma. If a patient has many moles, he needs to regularly visit a dermatologist and conduct an independent examination. If you identify an atypical mole or any changes in one of the moles, you should urgently visit a specialist.

Figure 3. UV protection.
Signs of malignancy
There are signs that contribute to the differential diagnosis of a mole and melanoma:
Asymmetry, when the halves of the nevus do not correspond to each other.
Blurred border, when the outline of the mole is jagged and uneven.
Nevi are unequally colored in various shades: yellow-brown, black, with an admixture of red, blue and white.
The size of the mole, nevi are often large, more than 5-6 mm in diameter. Melanomas are often found with a diameter of 3-6 mm.
Other important symptoms of melanoma that you need to pay attention to when examining a patient:
change in size, configuration, coloring of a mole;
the appearance of new elements on the skin;
increase in size;
addition of bleeding;
the appearance of nevus ulceration.

Figure 4. Smear for cytological examination.
During the examination, the doctor determines the size, configuration, coloring of all moles, the condition of the surrounding tissues, the presence of weeping or bleeding. Lymph nodes must be examined. A cytological examination is performed, tissue is collected using a “smear-print”. A biopsy is contraindicated if melanoma is suspected.
Treatment of melanoma
The choice of treatment method is determined by the stage of the disease.
Stage I
Surgical excision of the malignant neoplasm is performed within healthy tissue. The volume of excised healthy skin is determined by the depth of melanoma spread. Removal of regional lymph nodes does not improve survival rates for patients with stage I disease.
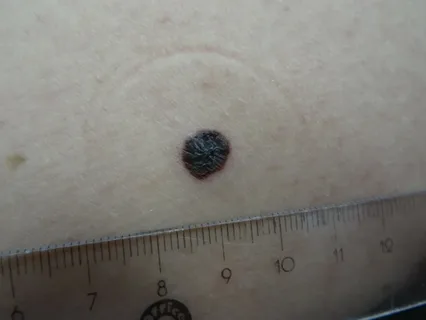
Figure 5. Patient examination.
Stage II
If there is a suspicion that melanoma has metastasized to the lymph nodes located near the tumor, a biopsy of one of them is performed; if the suspicion is confirmed, all remaining lymph nodes in the area are removed. Additional therapy with interferon alpha is recommended, and other drugs are prescribed to reduce the risk of melanoma recurrence. There is a tactic of routine removal of all lymph nodes near the tumor, its effectiveness has not been clinically proven.
Stage III
In addition to surgically removing the tumor itself, nearby lymph nodes are removed. Immunotherapy with interferon is carried out, which helps delay relapse. If a patient has several melanomas, all are excised. There are currently no effective treatment tactics for this category of patients. Specialists use radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and a combination of these methods.
IV stage
The patient at this stage cannot be cured. Only palliative treatment is possible.
If you are interested in this article, you will find even more useful information on all sections of dentistry on our website .