Endodontic treatment planning
Machine translation
Original article is written in RU language (link to read it).
Treatment planning in endodontics is a key point that requires the dentist to take an individual approach to each clinical situation. The specialist needs to objectively assess the condition of the tooth, take into account the patient’s opinion regarding the chosen method of therapy, and predict the effectiveness of treatment.
On the use of radiography in endodontic treatment at the webinar Digital Endodontics: Use of CBCT in Conservative and Surgical Endodontics .
Quality standard for endodontic treatment
The modern standard is based on the principles:
Painlessness of all manipulations for the patient.
Strict adherence to aseptic and antiseptic algorithms.
The passage, mechanical and medicinal treatment of the root canal, and then its obturation must be performed along the entire length of the canal.
Cleansing, mechanical and medicinal treatment are carried out without fail, regardless of the established diagnosis: pulpitis, periodontitis.
During the preparation of the canal, the latter must be expanded by two numbers or more, the apical third - to No. 25.
Obturation of the root canal is carried out with filler and sealant.
The filling material in the canal should tightly, without pores, fill the lumen of the canal all the way to the physiological apex.
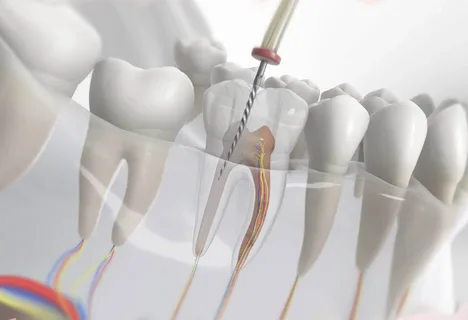
Figure 1. Endodontic treatment of a tooth.
Endodontic treatment planning
At the initial stage, the dentist needs to establish a diagnosis; it is made on the basis of not only basic treatment methods, but also additional examinations. The latter include:
X-ray examination;
electroodontodiagnostics;
thermal test.
X-ray examination
Despite the fact that X-ray diagnostics is an additional technique, it is mandatory during endotherapy. The endodontic treatment algorithm involves taking at least four radiographs during the treatment process:
diagnostic;
to calculate the working length of the channel;
to assess the quality of obturation, filling the entire network of canals with filling material;
to monitor long-term results of treatment, carried out in the next six months/year.
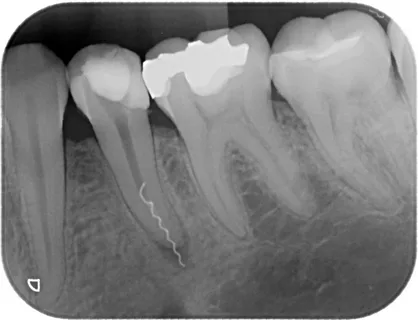
Figure 2. Radiography in endodontics.
If necessary, additional X-ray control can be performed, for example, at the stage of installing the main pin.
Reading a radiograph can be divided into objective and subjective.
The statement, or objective part, includes identifying signs of darkening or lightening when describing the anatomical structures of the tooth and adjacent tissues (coronal part, system of roots and canals, including the furcation zone, area of periapical tissues; integrity of the cortical plate; condition and structure of the bone).
Interpretation, or the subjective part, involves correlating clinical examination data (objective and subjective) with the results of radiography.
During endodontic treatment, the reference radiographic technique is long-focus radiography, but the most commonly used is intraoral contact radiography.
The technique of long-focus radiography is based on a significant distance from the object of interest of the beam tube. In this case, the scattering angle of the X-ray beam is minimal (the beam falls parallel), this makes it possible to practically eliminate distortions, or at least significantly minimize them. Today, this type of X-ray examination is performed using positioners in which the X-ray film and beam tube are located perpendicular to each other.
In the process of endotherapy planning, dental computed tomography is considered a promising radiography technique. Compared to orthopantomography, it has the following undeniable advantages:
The resulting image is highly informative (number and configuration of root canals, localization of the apical foramen, anatomical structure of the network of the main and additional canals, deltoid branches, the presence of pathological signs of inflammation in the periapical tissues, quality and density of obturation of the canal lumen).
Allows you to make the most reliable calculations of the sizes of certain anatomical structures.
Allows a specialist to evaluate any object of the maxillofacial zone within any section.
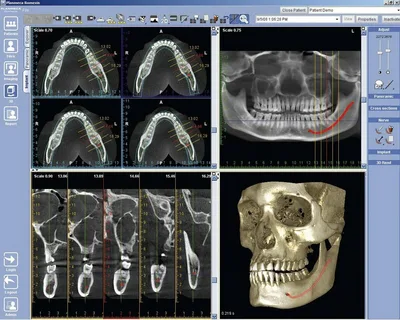
Figure 3. Computed tomography in dentistry.
It is worth mentioning that this diagnostic technique has some disadvantages:
relatively high cost;
Compared to orthopantomography, there is a slight increase in the radiation dose.
Thermal test
Identifying the sensitivity of a tooth to certain irritants (temperature and electrical) also helps to assess the condition of the pulp and its viability. But these tests do not allow one to reliably differentiate an intact pulp from an irreversible or reversible inflammatory process. This is due to the fact that areas of intact nervous tissue can persist even with severe necrosis.
Sometimes sensory tests show a positive result even against the background of destructive changes in bone tissue in the periapical area. But despite all these nuances, these tests are widely used to determine the vitality of the pulp, for this reason they are called vitality tests.
Figure 4. No water is used for the cold test.
The cold test is considered the most informative. The technique for performing it involves the use of additional means, these could be: ice cubes, dry ice, chloroethyl, frigen.
According to research data, application of cold for four seconds reduces tissue temperature to 25–30 °C, which provokes the development of a pain reaction. In this case, the pulp temperature drops by only 0.2 °C.
Ice has a temperature of about 0 °C, frigen, which is available in the form of a spray, is applied on a cotton ball to the cervical area - up to -40 °C, dry ice - up to -70 °C. There is some advantage to using dry ice when performing a cold test. Due to the layer of steam that is released from this substance at temperatures above 0 ° C, this test does not have a negative effect on the tooth itself and the tissues surrounding it. Cracks in the enamel do not appear even if the exposure to dry ice is prolonged, on the order of several minutes.
Sensitivity to heat of tooth tissue is assessed using heated gutta-percha (not filling pins, but special sticks with a high melting point) or heated wax.
It is worth mentioning that determining the sensitivity of a tooth to cold using a stream of water or air from a gun is not considered an informative technique.
The most sensitive part of the tooth for assessing the reaction to a cold stimulus is the cervical area of the tooth. Here, the thickness of the layer of hard tissue is the smallest, therefore the probability of an objective response of the pulp to a temperature stimulus is maximum.
Electroodontodiagnosis
EDI is an assessment of the electrical excitability of the pulp, which is based on the unique conductivity ability of hard tissues. The device creates a series of voltage pulses that are tuned to the resistance of the tooth tissue. Here, as with the thermal test, differential diagnosis is difficult. EDI allows you to reliably determine the vitality of a tooth.
Figure 5. EDI apparatus.
It is not possible to carry out differential diagnosis of different forms of pulpitis using EDI. For greater information, a comparative assessment of the electrical excitability of the pulp of several adjacent teeth is used.
EDI is more often used to assess the dynamics of inflammatory phenomena in the pulp, for example, pulp vitality after suffering a traumatic impact.
Factors leading to distortion of EDI results:
effect of anesthesia;
the patient is taking certain medications: analgesics, tranquilizers, bad habits: alcohol, drugs;
incomplete root formation, pathological resorption;
previous trauma;
large carious cavity or voluminous restoration;
inadequate interaction with enamel (filling material);
degenerative phenomena in the pulp, petrification;
inadequate response of the patient to a painful stimulus (children, patients suffering from mental disorders);
pulp necrosis, in which in different canals the pulp may or may not be vital (different values are determined on different tubercles);
the tooth is under a metal or ceramic crown.
It is also important to mention that electroodontic diagnostics is contraindicated in patients who have artificial pacemakers.
Based on the established diagnosis, taking into account the general condition of the patient, the material and technical equipment of the office, the doctor chooses a method of endodontic treatment.
Learn more about predicting the effectiveness of endodontic treatment at the webinar Success in endodontics: forecasting .


