Basics of surgical periodontology
Machine translation
Original article is written in RU language (link to read it).
Periodontal diseases of inflammatory origin are the most important and difficult to solve problem for dentists all over the world. According to research, the prevalence of periodontal tissue diseases among the adult population 35-44 years old is about 95%, and dysfunction of the dental system associated with tooth extraction due to severe forms of periodontal disease is observed approximately five times more often than with complications of the carious process.
Detailed protocols for the surgical treatment of periodontal diseases from world experts in the online course Surgical Periodontology .
Surgical treatment methods are widely used in the complex therapy of periodontal diseases. In many clinical situations, only surgical intervention can completely eliminate the inflammatory focus in periodontal tissues and prevent further destruction of bone tissue.
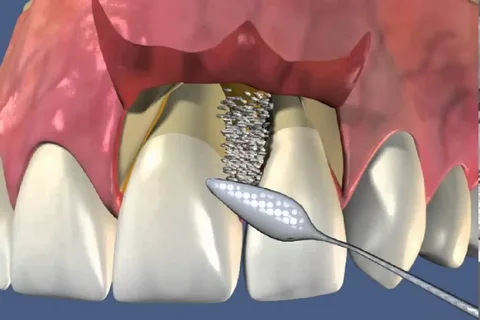
Figure 1. Gingival surgery.
General and local medications, orthopedic structures, and physiotherapeutic procedures are only additional components of the complex treatment of periodontal diseases, which make it possible to consolidate the positive effect achieved as a result of surgical intervention.
Surgical interventions on periodontal tissues are very diverse. Not least among them are preventive operations, the implementation of which helps prevent the development of periodontal diseases: vestibule plastic surgery, flap operations, curettage.
To date, the main developments in the field of surgical treatment protocols for periodontal tissues are aimed at sanitizing periodontal pockets, effectively inhibiting bacterial microflora and increasing the activity of the osteogenesis process. Surgical periodontology aims to improve the structure and functioning of the periodontium.
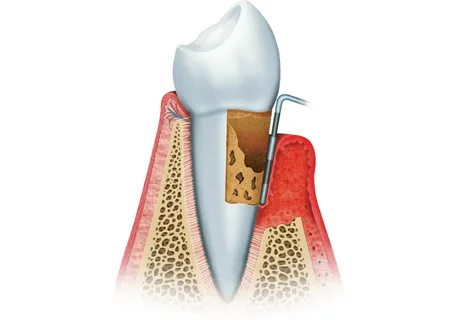
Figure 2. Periodontal disease.
Fundamentals of periodontal surgery:
gentle excision of soft tissue to protect the graft and alveolar process;
preservation of bone fragments of alveolar processes damaged as a result of osteoporosis;
thorough elimination of granulations and proliferated epithelium;
gentle manipulation of the cement of the tooth root;
reliable hemostasis, control over the preservation of blood supply to the flaps, prevention of tension on the flaps;
elimination of local aggravating factors.
What is gingival surgery
Gingival surgery is a set of surgical manipulations on periodontal tissues that can be performed on free and attached gums, these include the following:
curettage;
interventions that correct the gum edge;
gingivotomy;
gingivectomy;
operations using cryodestruction, piezosurgery, electrocoagulation, laser coagulation;
patchwork operations;
gingivoplasty;
surgical interventions of secondary engraftment;
osteogingivoplasty using drugs that have a stimulating effect on bone tissue repair;
mucogingival surgery, which includes interventions such as frenulotomy, frenulectomy, deepening of the vestibule;
mucogingivosteoplasty, which is a combination of gingivoplasty, osteoplasty and plastic surgery of the oral vestibule;
odontoplasty.
Figure 3. Sanitation of the oral cavity.
Preoperative preparation activities
At the first stage, it is important to teach the patient individual oral hygiene. It is recommended to organize follow-up examinations, during which the doctor will evaluate the quality of the patient’s hygiene; their duration is one month before surgery and six months after it. Poor hygiene often causes recurrence of the disease or ineffective surgery. During the entire period of dynamic observation, the patient is recommended to brush his teeth 3 times a day, and the duration of each brushing should be at least three minutes. Cleaning time: before breakfast and after, before bed. It is important that the patient pays attention during brushing to the teeth that are located in the area of the excretory ducts of the salivary glands (lingual surfaces of the lower incisors, buccal surfaces of the upper molars); interdental spaces are cleaned with floss; toothpicks are allowed in hard-to-reach places. During this period, it is better to take a brush with hard bristles; only after the operation it is changed to soft for a period of no more than seven days. The hard palate and tongue are contaminated with pathogenic microflora; their cleansing is mandatory not only for periodontal diseases.
At the second stage, supra- and subgingival dental plaque is removed with mandatory local antimicrobial treatment. An ultrasonic scaler is indispensable for removing subgingival deposits and cleaning periodontal pockets from granulations. Performing this procedure is of utmost importance, since during the formation of a periodontal pocket, the periodontal attachment is disrupted. Pathogenic microflora and the products of its metabolism have a destructive effect on the ligamentous apparatus and bone tissue of the alveolar process. And the developing subgingival deposits aggravate the destruction. It is necessary to monitor the quality of hygiene and, if necessary, repeat the professional cleaning procedure throughout the entire period of treatment and observation.
At the third stage, the oral cavity is sanitized. It consists of treating teeth affected by caries, replacing failed restorations, removing teeth with the third and fourth degrees of mobility, and getting rid of low-quality dentures in the presence of galvanism. In the process of filling cavities located in the area of the gingival margin, it is important to qualitatively restore contact points to prevent injury to the gingival papilla, prevent the accumulation of bacteria and the formation of tartar.
At the fourth stage, the mobile teeth are fixed and the lost functional balance is restored, which is possible thanks to the production of splinting structures. The supporting apparatus of the tooth is significantly weakened due to the destruction of bone tissue. Teeth become sensitive even to small loads, which become a traumatic factor and aggravate further destruction. Immobilization must be performed before surgery, since loose teeth will cause injury to the blood clot and slow down reparative regeneration.
At the fifth stage, teeth are selectively ground to level the occlusal plane and get rid of traumatic occlusion. Supracontacts contribute to the formation of vertical foci of periodontal destruction. In a third of patients, the formation of traumatic nodes is observed if the enamel bumps are not erased. The influence of this factor especially increases in patients over 25 years of age, since at this age the buffer parameters of the periodontium decrease. The most popular among practicing dentists is selective grinding of teeth using the Jenkelson method.
In the case of previous multiple removals, the preparation of immediate prostheses is required at the preparatory stage.
If there is a suspicion of exposure of the neurovascular bundle in the periodontal tissues or the electrical excitability of the pulp decreases, this indicates the need for tooth depulpation.
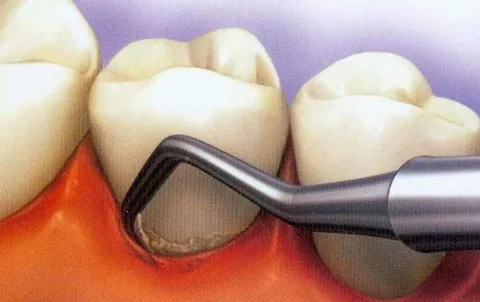
Figure 4. Professional oral hygiene.
Anesthesia in surgical periodontology
Adequate pain relief is the most important stage of any surgical intervention. Anesthesia is indicated even for simple manipulations, since even minor pain during surgery negatively affects wound healing and long-term results. The choice of type of anesthesia is determined by the volume of intervention and the general condition of the patient.
Figure 5. Administration of anesthesia.
Anesthesia must be regarded as the prevention of possible complications during the operation. Carpule anesthetics are most effective. The small diameter of the needle prevents the formation of a mucosal defect during infiltration anesthesia. Highly effective anesthetics (mepivacaine, articaine) are effective in minimal quantities, which reduces the amount of hydropreparation and trauma to the mucosa. The duration of action of anesthetics allows one anesthesia to be performed, which will be sufficient until the end of the operation. The use of an anesthetic with a vasoconstrictor ensures hemostasis of the surgical field, and after their effect ends, blood filling of the wound is observed.
If you are interested in this article, pay attention to the detailed course on the surgical treatment of periodontal diseases Surgical periodontology: preparation for prosthetics .


