Precancerous diseases of the oral mucosa
Machine translation
Original article is written in RU language (link to read it) .
Precancerous diseases are pathological changes in the oral mucosa, which under certain conditions can transform into cancer, but are not yet an oncological disease. These are conditions that lack several morphological features to allow a diagnosis of a neoplasm to be made.
Always up-to-date information on all sections of dentistry is available on our website .
All precancerous diseases of the oral mucosa or red border of the lips can be divided into the following two groups:
Obligate precancers - Bowen's disease.
Optional precancers – leukoplakia, papillomatosis and others.

Figure 1. Lesion element on the red border.
Bowen's disease
Bowen's disease, other names for this disease - erythroplakia, erythroplasia, is an obligate precancer that can affect the red border of the lips, as well as the oral mucosa.
Typical clinical picture
The pathological focus is predominantly single, has the appearance of a hyperemic bright red spot, the surface of which is velvety, due to the smallest papillary growths, or smooth. In the center of the lesion there is a separate zone with areas of keratinization, the surface of which is finely lumpy. Gradual atrophy of the mucosa in this area leads to its retraction relative to the surrounding tissues, and erosion may occur.
The pathological focus can be small in size - 2-3 mm, but in some situations it can reach 5-7 cm; the configuration of the lesion is irregular, without clear boundaries.
When making a diagnosis, it is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis with the following diseases:
leukoplakia,
lichen planus,
syphilis,
lupus erythematosus,
traumatic erythema.
Papillomatosis
Papillomatosis belongs to the group of facultative precancerous conditions; it often occurs against the background of exposure to any traumatic factor over a long period of time.
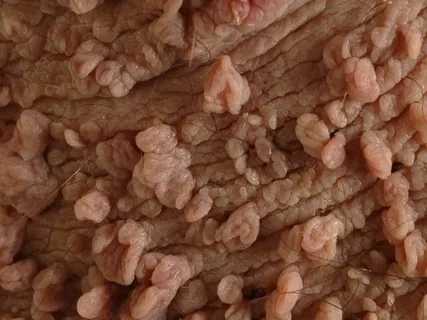
Figure 2. Papillomatosis on the skin.
Typical clinical picture
This pathological formation rises somewhat above the adjacent mucosa and has a wide base, which is located on a thin stalk. The formation has a bumpy surface, but in rare cases it is smooth. If the process of keratinization occurs, in this case the surface of the papilloma acquires a grayish-white tint, and its appearance becomes similar to “cauliflower”.
Papillomas are predominantly localized on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, palate, and tongue.
Papillomas are distinguished:
Non-keratinizing, have a soft consistency, painless on palpation, pale pink in color.
They are keratinizing and have a denser structure and a whitish tint.
The surrounding mucosa is often moderately hyperemic, and signs of an inflammatory reaction are detected.
Symptoms of malignancy of papillomas:
the base becomes more dense;
mobility is limited,
signs of keratinization increase,
cracks appear on the surface,
starts to grow
Spontaneous bleeding is possible.
When making a diagnosis, it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis with the common wart.
Warty precancer
Warty precancer belongs to the group of obligate precancerous diseases of the red border of the lips.
Figure 3. Cracked lower lip.
Typical clinical picture
Externally, this pathological formation has the appearance of a clearly limited hemisphere, the diameter of which varies from 5 mm to 10 mm. It rises somewhat above the surrounding tissues of the lip, its consistency is dense.
The predominant localization is exclusively the red border, in most cases - the lower lip.
The color of the formation is often no different from the color of the surrounding tissues, but may acquire a gray-reddish tint. Its surface is dotted with small, tightly fitting gray scales.
The red border adjacent to the pathological lesion has no morphological changes and is painless on palpation. The formation looks like a papilloma or wart.
This precancerous condition is characterized by rapid malignancy within several months after its appearance. Symptoms of malignancy are clinically difficult to interpret, in some cases impossible, among them the following can be distinguished:
the base of the formation is compacted,
increases sharply in size,
excessive keratinization occurs,
the surface is exposed.
When making a diagnosis, it is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis with the following diseases: common wart, papilloma, keratoacanthoma, pyogenic granuloma.
Limited hyperkeratosis
Pathological formation, belongs to the group of obligate precancerous diseases, affects the red border of the lips.
Characteristic clinical picture
Limited hyperkeratosis is characterized by a lesion element in the form of a limited polygonal lesion, the diameter of which can be 10 mm, or can be more extensive, reaching 1-1.5 cm. The pathological area is clearly demarcated from the surrounding tissues of the lip, somewhat recessed relative to neighboring areas, the surface of the lesion smooth, covered with tightly welded scales. Against the background of excessive keratinization, the lesion acquires a grayish-white tint. Palpation reveals a noticeable compaction, which in shape corresponds to a thin plate. The surrounding red border is painless and soft on palpation.
When making a diagnosis, it is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis with the following diseases: leukoplakia, lupus erythematosus, lichen planus.
Keratoacanthoma
It is an optional precancer, a disease that has a viral etiology (human papillomavirus).
Characteristic clinical picture
The predominant localization is the skin, but can occur on the red border and mucous membrane of the oral cavity. The lesion is single, resembles a flattened node, most often has the shape of a hemisphere, in the center of the formation there is a crater-shaped depression filled with keratinized masses, on the outside it is surrounded by an epithelial shaft.
The formation rapidly increases in size, reaches 2-3 cm in diameter, and its palpation is painful. The consistency of keratoacontoma is elastic. If you peel away the dirty gray mass, a dry, fluffy, non-bleeding crater bottom is revealed. No reaction from the lymph nodes is observed.
There are known cases of self-healing of keratoacanthoma within a few months to six months, without scars.
Symptoms of malignancy:
the appearance of infiltration at the base,
the addition of bleeding, most often when trying to clear the formation of horny masses.
When making a diagnosis, it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis with the following diseases: squamous cell carcinoma, papilloma, cutaneous horn, wart vulgaris, warty precancer.
Cutaneous horn
Refers to facultative precancerous diseases, the appearance is associated with senile atrophy, keratoma, and can develop on scars, areas affected by leukoplakia, against the background of senile warts.

Figure 4. Cheilitis.
Characteristic clinical picture
Clinically, a single dense horn is detected, cone-shaped, gray or grayish-brown in color. The formation rises above the surrounding tissues by more than a centimeter. The formed horny masses resemble horn in density, configuration, and layered structure. When you try to remove the horny masses, the ulcerative surface is exposed. The pathological focus can exist for years and is capable of malignancy.
When making a diagnosis, it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis with keratoacontoma. When making a diagnosis, they are guided by the data of the anamnesis and histological examination.
Mangannotti abrasive cheilitis
It is an obligate precancer, affecting mainly older men who have a bad habit - smoking, as well as patients with chronic diseases of the digestive system.
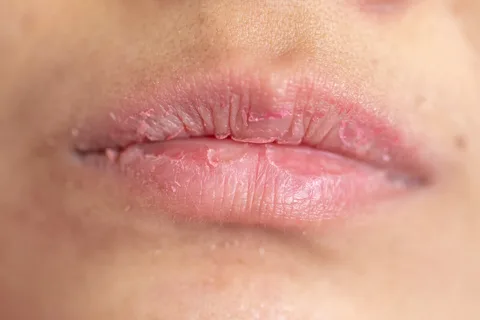
Figure 5. Peeling on lips.
Predisposing factors:
injury,
frequent exacerbations of herpes infection,
excessive insolation.
Typical clinical picture
Typical localization is the lateral areas of the lip. The pathological element is a single erosion, of irregular configuration, in the shape of an oval, the size in diameter is from 5 to 10 mm, the surface is smooth, polished. Erosion may become crusty. The surrounding tissues are not subject to changes, there are no compactions or inflammatory changes.
Often erosion epithelializes and then recurs again in the same place.
Symptoms of malignancy:
seal at the base
deepening erosion.
In this case, malignancy can occur within several months from the onset of the disease.
When making a diagnosis, it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis with the following diseases: lupus erythematosus, erosive form of lichen planus, leukoplakia, herpes, pemphigus, actinic cheilitis.
There is even more information on various diseases of the oral mucosa in the Periodontology Training section of our website.
