Periodontal surgery, classification and review of operations
Machine translation
Original article is written in RU language (link to read it) .
In the complex treatment of periodontal diseases, surgical treatment is the main stage, since it eliminates the cause of the disease and eliminates recurrence, which cannot be achieved with conservative methods alone.
A detailed course on the surgical treatment of periodontal diseases . Surgical periodontology: preparation for prosthetics .
All periodontal surgical interventions can be grouped into the following groups:
gingival surgeries,
osteomucogingival,
mucogingival.
Gingival surgeries
The concept of gingival surgery includes the following surgical interventions:
curettage,
gingivotomy,
gingivectomy.
Curettage
Curettage involves complete scraping of tartar, granulations, modified epithelium, and destroyed cement from the pathological periodontal pocket using a special set of tools. The purpose of the operation is to obtain a clean wound surface.
Indications for curettage are the presence of pockets, the depth of which does not exceed 6 mm, the absence of bone loss, and dense gums in the area of the proposed surgical intervention.
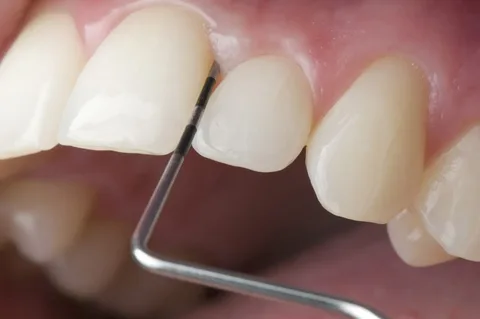
Rice. 1. Diagnosis of the depth of the periodontal pocket.
Contraindications for curettage
The pocket depth is more than 6 mm.
Acute inflammation, abscess formation.
Teeth with degree 3 or 4 mobility.
Fibrous, thinned gums.
The closed curettage protocol is performed with a pocket depth of up to 4 mm.
Local anesthesia
Removing dental plaque from the tooth surface with curettes or a pointed excavator, polishing the root with a scaler.
Next, granulations and modified tissue are scraped from the inner wall of the periodontal pocket.
We rinse the treated pocket with sterile saline solution.
When a blood clot forms, apply a protective bandage for 7-8 days.
If the outcome is favorable, the clot is organized, the gums contract, and the pocket depth decreases.
The disadvantage of the technique is that it is impossible to assess the quality of removal of pathologically changed tissues; some manipulations are carried out blindly.
Open curettage protocol
It was developed to prevent the disadvantages characteristic of closed curettage, the technique allows you to work with pockets up to 6 mm, involves more thorough removal of granulations and dental plaque from the pathological pocket, and guarantees visual control.
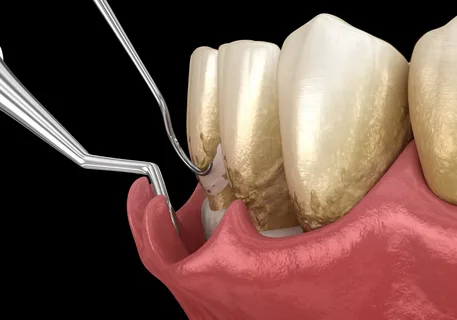
Rice. 2. Method of performing open curettage.
At the preliminary stage, dental plaque is removed, then anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out for a week.
Stages of open curettage
Local anesthesia.
A scalpel incision beveled inwards is made with a scalpel to the entire depth of the pocket.
The flap is peeled off, and the final removal of dental plaque, granulations, and modified epithelium is carried out.
The intervention area is washed with sterile saline solution.
After a blood clot has formed, the flaps are placed in place.
The wound is sutured with interrupted sutures in the interdental spaces.
A protective periodontal bandage is applied for three days.
Gingivotomy
Gingivotomy is a surgical procedure related to periodontal surgery that involves cutting the gums.
Indications
periodontal abscess,
narrow and deep pathological periodontal pockets.
Gingivotomy protocol
Local anesthesia.
A scalpel is used to vertically dissect the wall of the pocket to its base.
Using a rasp, the gingival margin is separated, then the remaining dental deposits are removed, granulations and modified epithelium are scraped out from the walls of the pocket with a curettage spoon.
After rinsing with a sterile solution, the flaps are placed in place and sutured with interrupted sutures.
If the patient has a periodontal abscess, it is better to perform a horizontal incision, in which the tissue is dissected along the lower pole of the inflammation. Then the cavity is washed with antiseptic solutions and drainage is applied.
Gingivectomy
Gingivectomy is a surgical procedure related to periodontal surgery that involves excision of the gums.
Types of gingivectomy:
simple,
partial,
radical.
Indications for simple gingivectomy
pockets more than 5 mm in the presence of uniform horizontal loss of bone,
fibromatosis of the gums,
hypertrophic gingivitis,
performing patchwork operations,
lengthening before orthopedic treatment of the clinical tooth crown.
Contraindications for gingivectomy
a narrow area of attached gum,
deep bone pockets.
Gingivectomy protocol
Local anesthesia.
In the area of all teeth located in the surgical intervention area, the depth of the pockets is determined.
The walls of the pockets are dissected with a scalpel at the level of the bases, the incision is made scalloped, following the contour of the gums. The interdental areas of the gum are excised, the marginal ones are removed with a curette.
The exposed root surface is polished.
Hemostasis is performed using gauze pads, and the wound surface is covered with a protective bandage for a period of 2 weeks. By the time the protective bandage is removed, complete epithelization occurs and the formation of a dentogingival attachment occurs.
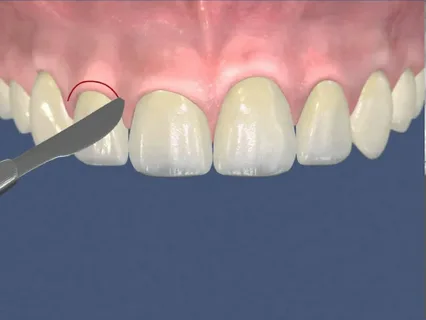
Rice. 3. Shape of the incision for gingivectomy.
Osteomocogingival surgeries
Another name for this group of operations is patchwork; they are performed in the presence of pockets whose depth is more than 6 mm. Their main goal is the elimination of pathological pockets, restoration of periodontal attachment and bone renewal.
All existing dozens of modifications of flap operations are based on one single technique according to Cieszynski-Widman-Neumann, during which a mucoperiosteal flap is cut out and exfoliated, tooth roots are polished, bone pockets are treated, and the inner wall of the flap is de-epithelialized.
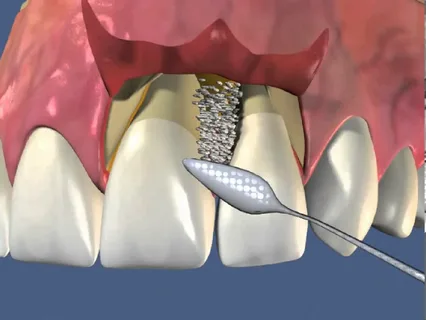
Rice. 4. Scheme of the flap operation.
Advantages
thorough removal of modified tissues thanks to the possibility of visual control,
guarantee of long-term stabilization of the pathological process.
Flaws
high morbidity,
exposure of the necks of the teeth,
the appearance of sensitivity,
cosmetic defect due to disruption of the contours of the gingival papillae,
tooth mobility.
Furcation plastic surgery
A technique aimed at removing the inflammatory focus from the bifurcation area of the chewing teeth and preventing relapses.
Stages
Formation of a mucoperiosteal flap, gaining access to the furcation area.
Removal of dental plaque, removal of granulations.
Odontoplasty, grinding of tooth tissue, widening the narrow entrance to the furcation zone.
Osteoplasty - correction of bone contour.
Returning the flap to its place, suturing.
The surgical intervention will be considered successful if a tunnel is formed in the furcation area, sufficient for treatment with dental brushes, covered by a soft tissue papilla at rest.
Apical displacement of the flap
The peculiarity of this type of surgical intervention is the restoration of the scalloped contour of the gums, the creation of such an architecture of the gums and bone, when the bone is higher in the interdental spaces. It is carried out through apical displacement of the flaps and the application of periosteal sutures.
Guided regeneration of periodontal tissues
Indications
lesions in the furcation area,
presence of gum recession,
2- and 3-wall periodontal pockets,
the need for correction of the alveolar ridge,
sinus lift,
the presence of peri-implantitis or bone dehiscence.
The traditional method of directed regeneration involves the use of a special membrane, which will act as a physical barrier. A physical barrier is necessary to prevent apical proliferation of the epithelium and the formation of connective tissue during the healing stage of the defect in the osteoplastic material.
Preference should be given to absorbable membranes to avoid repeated surgery.
Mucogingival surgeries
This group includes the following surgical interventions:
frenulotomy,
frenulectomy,
frenuloplasty,
vestibuloplasty,
operations to eliminate recessions.
Frenulotomy involves a transverse dissection in the middle third of the frenulum of the tongue with sharp scissors under local anesthesia, performed in infancy.
The frenulectomy technique is based on two semi-oval vertical incisions, excision of the frenulum, mobilization of mucous flaps, and suturing.
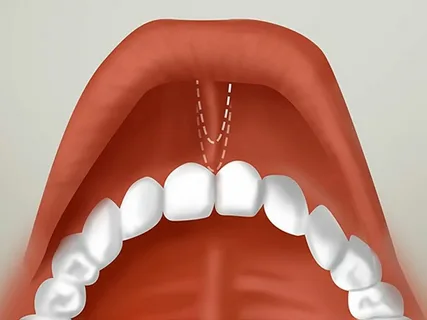
Rice. 5 Scheme of frenulectomy.
Frenumplasty is based on the formation and subsequent dispersion of triangular tissue flaps to correct a short frenulum.
Vestibuloplasty involves the displacement of the facial muscles, which are attached to the crest of the alveolar process, to deepen the vestibule of the oral cavity.
Surgical elimination of recession is possible only if the patient has a class 1 or 2 recession. Today, there are many different techniques aimed at eliminating recession.
Pay attention to the complete course on the treatment of recessions Treatment of recessions: all types of flap operations and tunnel technique .
