Opening of the tooth cavity. Endodontic access
Machine translation
Original article is written in RU language (link to read it) .
A key factor in successful endodontic treatment is ensuring adequate access to the tooth's root canal system. Every dentist, when starting endodontic treatment, should strive to create the most direct access to the canal orifices.
Learn more about endodontic access in the webinar Access to the root canal system .
In this article we will consider the most current methods for creating access, which guarantees maximum quality of subsequent instrumental processing of the root canal system.

Rice. 1. With high-quality access, the entire nerve is removed.
Fundamental points that every endodontist must consider
The pulp chamber is always located in the very center of the tooth; its miniature contours correspond to the external configuration of the tooth in the area of the cemento-enamel junction. Before beginning the formation of endodontic access, it is important to clearly understand the configuration of the tooth cavity in the area of the enamel-cement interface. The pulp chamber will be located exactly in the center of the contour of the cemento-enamel junction. The opening of the tooth cavity occurs pointwise, then it is necessary to excise the entire roof of the pulp chamber, in accordance with the contour of the boundary of cement and enamel. Experts recommend accessing the pulp chamber before the stage of applying a rubber dam, the absence of which guarantees optimal visualization of the configuration of the enamel-cement interface. And when full access has been created, infected tissue and failed restoration have been removed, then you can begin to apply a rubber dam.
In the course of many years of research, it has been proven that the mouths of the canals are always determined at the border of the darker bottom of the pulp chamber and its lighter walls, mainly at the corners of the bottom of the tooth cavity. Access is adequate only if the boundary between the dark shade of the tissues of the bottom of the tooth cavity and the lighter shades of the walls of the tooth cavity is clearly formed. If such a distinction is absent, this indicates incomplete removal of the roof of the pulp chamber, and the opening stage should be continued. When endodontic access is adequately created, using an endodontic probe with a sharp tip, the orifices of the canals, which are located in the corners of the bottom of the pulp chamber, are easily identified. Preparation of the bottom of the pulp chamber using burs is possible only after identifying obliteration of the canal orifices. In the vast majority of cases, canal orifices are easy to detect with an endodontic probe.
The mouths of the canals of a multi-rooted tooth are located symmetrically relative to one another. Having determined the mouth of the canal on one side, you can draw an imaginary line along the bottom of the pulp chamber in the mesio-distal direction; at an equal distance on the other side of this line there will be a second mouth. When the canal mouth is localized exactly on an imaginary line, this canal is the only one; there is no need to look for an additional one.
Opening and opening the tooth cavity
Opening and opening the tooth cavity are those manipulations that are mandatory stages of the endodontic treatment protocol; without them, it is impossible to adequately remove the pulp from the pulp chamber and the root canal system. Opening the tooth cavity during the treatment of pulpitis or periodontitis guarantees access to the mouths of the canals, necessary for instrumental and antiseptic treatment.

Rice. 2. Endodontic access.
In the vast majority of cases, these manipulations are performed through a carious cavity. In some situations, it is necessary to trephine the crown of an intact tooth.
The stage of opening and opening the tooth cavity includes the following sequential manipulations:
Opening the carious cavity involves, in addition to excision of all infected tissues, the removal of overhanging edges of the enamel that do not have support in the form of intact dentin, in order to provide free and convenient access to the future surgical field.
Excision of the bulk of infected dentin destroyed by caries. Thinning of the suprapulpal area of dentin.
Forming access to the inflamed pulp tissues through a targeted opening of the roof of the pulp chamber, is carried out with the tip of a probe or a spherical bur No. 1. There should be a feeling of “falling through” into the chamber cavity.
When the vault of the chamber roof is opened pointwise, it is recommended to continue opening with the help of burs; burs in the shape of a ball or fissure are suitable for this manipulation.
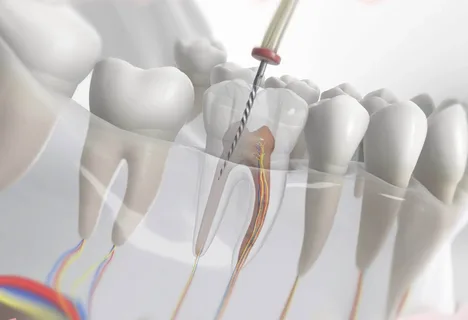
Rice. 3. Endodontic access to the mandibular molar.
A ball-shaped bur is inserted into the cavity and the roof of the cavity is excised.
The fissure bur is inserted through the trepanation window and the roof of the pulp chamber is removed using circular movements along the walls of the prepared cavity. The manipulation is carried out under the control of a dental mirror; probing of the root canal mouths is carried out with an endodontic probe.
If the opening of the cavity is insufficient, the overhanging edges are not completely removed, this will entail incomplete subsequent amputation of the infected pulp tissue.
The volume of access directly depends on the size of the patient’s dental pulp chamber. In older people, the pulp volume is significantly less than in young people.
A mandatory criterion for the quality of tooth cavity opening is the formation of adequate access to the root canal system, which guarantees free penetration of endodontic instruments into the canals. If the tooth cavity is not opened enough, this will significantly complicate the insertion of files into the canal, which will lead to breakage of the files.

Rice. 4. Formation of endodontic access in the premolar.
Excessive excision of the pulp chamber tissue will cause weakening of the walls of the crown, which can lead to such a serious complication as its fracture, especially under the influence of intense chewing load.
Quality criteria for generated access
the walls and bottom of the pulp chamber are easily visible and accessible to endodontic instruments;
the prepared cavity connects smoothly, without sharp boundaries or transitions, to the walls of the pulp chamber;
the canal mouths are easily visualized, access to them with an endodontic probe is not limited in any way;
the probe slides freely along the wall of the tooth cavity.
Features of access depending on the group affiliation of the tooth
It is advisable to consider the nuances of preparation and opening of the tooth cavity in different groups of teeth, to find out the features that are important for the dentist.
Features of trepanation of incisors and canines
If contact surfaces are affected by the carious process, access to the pulp chamber is made from the palate or tongue.
We use the same access for trephination of intact upper incisors, or in case of carious lesions in the cervical area.
Trephination is carried out with a turbine tip and a diamond-coated bur in the center of the middle third of the tooth crown.
Trephination of incisors from the cutting edge is unacceptable; there is a risk of breaking off the vestibular or lingual wall.
The intact upper lateral incisors are trepanned in the area of the blind fossa. The direction of the bur when opening the pulp chamber is perpendicular to the palatal or lingual surface; when opening, the direction of the bur should be parallel to the axis of the tooth.
Trephination of the crown of the lower incisor is carried out not in the center, but closer to the cutting edge; the lingual inclination of the tooth must be taken into account.
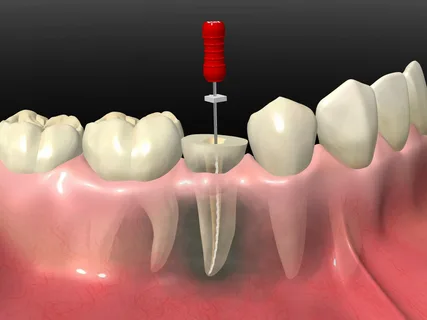
Rice. 5. Unobstructed access to the root canal.
Features of premolar trephination
When premolars are damaged by a carious process on the contact surfaces, the cavity is brought to the chewing surface, and the opening is carried out at the bottom of the carious cavity closest to the pulp.
In case of an intact premolar or a carious process in the area of the tooth neck, trepanation is performed in the middle of the fissure, towards the buccal horn, this is the closest path to the pulp. The opening continues in the bucco-palatal direction.
It is important to consider that the bottom of the pulp chamber is located under the gum, above the neck of the tooth.
When opening lower premolars, it is important to remember the lingual inclination of the crown relative to the root to avoid perforation of the lingual wall.
Features of trephination of molars
Trepanation of the first upper molar is performed in the anterior fissure, opening - in the bucco-palatal direction.
The most complications arise when opening the second and third upper molars, which is due to the variability in the structure of their crowns, which often have a crown elongated in the anteroposterior direction.
Trepanation of lower intact molars is carried out in the middle third of the longitudinal fissure. The opening is performed in the anteroposterior direction.
The contour of the tooth cavity of the lower first molars has the shape of a trapezoid.
The second and third molars of the mandible have a triangular cavity shape.
All methods for creating ideal endodontic access and practical recommendations in the online lesson Endodontic access: from simple to complex .
