Manifestations of viral infections in the oral cavity
Machine translation
Original article is written in RU language (link to read it) .
The most common infectious viral diseases that are accompanied by clinical manifestations in the oral cavity are acute herpetic stomatitis and chronic recurrent herpes. In this article we will dwell in detail on other infectious diseases.
Find a large selection of webinars and online courses in various areas of dentistry on our website .
Herpes zoster
Herpes zoster is a viral disease accompanied by damage to the skin and nervous tissue, manifested as a result of reactivation of the herpes virus type 3, herpes zoster. The virus is neurodermatotropic.

Rice. 1. Herpes on the upper lip.
The clinical picture is characterized by the appearance of inflammatory elements on the skin, these are predominantly blistering rashes against a background of erythema, as well as damage to nervous tissue (dorsal roots of the spinal cord and ganglia of peripheral nerves).
In people with immunosuppression, the risk of developing this disease is tens of times greater than in patients with stable immunity.
Immunosuppressive conditions that increase the risk of herpes zoster include:
bone marrow transplantation,
HIV infection,
chemotherapy,
leukemia,
taking systemic glucocorticosteroids.
Women, elderly patients, and people who, for one reason or another, have weakened defense mechanisms are more often susceptible to the disease.

Rice. 2. The appearance of the lesion is preceded by pain.
Routes of transmission of this infection:
contact,
airborne.
Clinical manifestations
It is more often observed in the autumn-winter period.
Accompanied by fever.
The pain is of a neuralgic type.
Erythematous-vesicular rashes appear on the skin and mucous membranes, which spread along the affected peripheral nerves.
The intensity of pain may be insignificant, without pronounced pain, paresthesia, or burning, cutting, paroxysmal neuralgic pain along the affected nerves may be observed. Various irritants provoke increased pain.
At the same time, body temperature begins to increase to 38-39°C, headache, malaise, and chills appear. After 1-5 days from the onset of pain, the following symptoms develop: edema develops, hyperemia occurs at the affected area, against which grouped vesicles are diagnosed, their size does not exceed 5 mm, they contain transparent exudate. On the skin, the vesicles dry out and turn into crusts.
Along with the skin, pathological changes are also observed on the oral mucosa, which becomes markedly hyperemic; numerous vesicles appear along the affected nerve; they open almost immediately, leaving behind erosions covered with fibrinous plaque.
Erosion on the mucous membrane epithelializes, leaving no traces behind, and temporary pigmentation remains on the skin after separation of the crusts. The entire period of clinical manifestations lasts up to 3 weeks.
Herpangina
An acute infectious disease caused by enteroviruses (ECHO, Coxsackie). The incidence is higher among children.
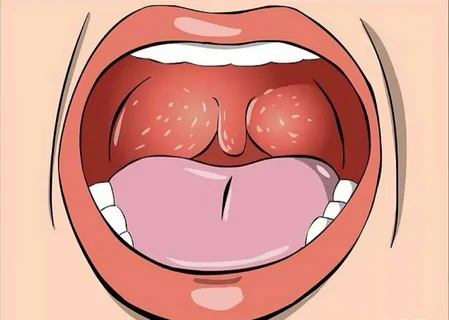
Rice. 3. Symptoms of herpetic sore throat.
Clinical manifestations
Acute onset.
Increase in body temperature to 39.5°C.
Pain when swallowing.
Headache.
Slight enlargement of regional lymph nodes, their palpation is painless.
The mucous membrane is moderately hyperemic.
Blistering rashes on the mucous membrane.
Typical localization of rashes: anterior arches, uvula, tongue, soft palate.
General treatment is carried out by internists; the following drugs are locally relevant:
painkillers,
antiseptics,
proteolytic enzymes,
keratoplasty,
antiviral drugs.
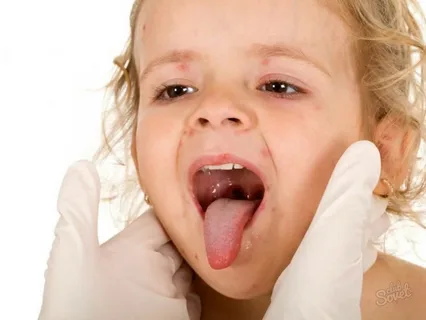
Rice. 4. Examination of the child for rashes.
Flu
This infectious disease can be caused by various types of RNA-containing viruses, with the exception of adenoviruses, which are DNA-containing.
Characteristic clinical manifestations
The mucous membrane is hyperemic.
The severity of the vascular pattern is noted.
Swelling and hemorrhages occur.
A coating appears on the tongue and desquamation of the epithelium may be observed.
Small bubbles containing exudate appear on the mucosa, which quickly open to form bright red erosions, sharply painful on palpation.
Rarely, large blisters up to 2 cm may form.
The severe acute form of the disease is characterized by serous stomatitis, accompanied by small hemorrhagic spots on the mucous membrane.
The diagnosis is established on the basis of anamnesis, examination and histological examination.
foot and mouth disease
This is an infectious disease caused by a filterable virus. Humans become infected from animals due to consumption of meat and dairy products. Cases of infection by airborne droplets in the presence of injuries to the skin and mucous membrane are rare.
Characteristic clinical symptoms
General weakness.
Headache and muscle pain.
Temperature.
Burning of the oral mucosa.
Salivation.
On the second day, small bubbles appear on the hyperemic and edematous mucosa, which quickly open to form aphthous-like elements.
Typical localization of lesions: gums, tongue, palate, lips.
Rarely, symptoms appear on the mucous membranes of the eyes, nose, and genitals.
Skin lesions of the following localization are often associated: wings of the nose, soles, interdigital folds, bases of nails.
Clinical manifestations are observed within several weeks. The diagnosis is established on the basis of anamnesis and clinic. Treatment is carried out on the basis of an inpatient infectious diseases hospital. Local therapy involves preventing the addition of a secondary infection.
Chicken pox
The causative agent of this infectious disease is a filterable virus.
Characteristic clinical symptoms
Absence of prodromal phenomena, acute onset.
Temperature.
Skin rashes are observed throughout the body and scalp.
Simultaneously with skin rashes, lesions, blisters, appear on the oral mucosa on the tongue, gums, lips, and hard palate.
The blisters quickly open with the formation of small, round, gray-pink erosions that look like aphthae.
False polymorphism is characteristic, which is explained by the staged appearance of rashes at intervals of several days.
The disease resolves within 3-4 days.
Treatment is carried out in an infectious diseases hospital. The following drugs are locally effective:
painkillers,
antiseptics.
Measles
The causative agent of measles is a filterable virus, infection is carried out by airborne droplets. It is important to consider that patients are most contagious in the last 2 days of the incubation period and during the three days of illness.
Clinical symptoms
General intoxication.
Fever.
Rash.
Conjunctivitis.
Inflammation of the upper respiratory system.
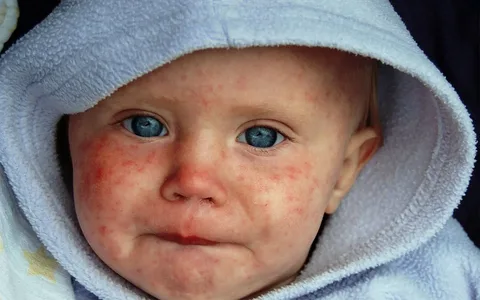
Rice. 5. Skin manifestations of measles.
On the hyperemic mucosa during the prodromal period, often on the cheeks, less often on the gums and lips, whitish-yellow dots appear (resemble drops of lime splashed against the background of hyperemia). Their size is up to 2 mm, they rise slightly above the surrounding tissue and do not merge with each other. These are Filatov-Koplik spots, which disappear within 3-4 days, but at the same time measles enanthema appears on the skin. The latter is also observed on the mucous membrane of the soft palate: rashes of pale red and bright red spots that have a round or elongated irregular shape.
Infectious mononucleosis
The causative agent of the disease is the Epstein-Barr virus, a DNA-containing lymphoproliferative virus of the herpes virus family. Distribution occurs by lymphogenous and hematogenous routes. The source of infection is a virus carrier or a sick person.
Clinical symptoms
Angina.
Fever.
Adenosplenomegaly.
Children and young people are more susceptible to this disease; older people rarely get sick. The incubation period lasts from two to three weeks. The disease is accompanied by damage to the lymphatic tissue, the leukocyte formula shifts to the left, and elements of the lesion appear on the oral mucosa.
The onset of the disease is acute: general malaise, fever, lymph nodes are enlarged, mobile, painless, inflammation of the lymphoid tissue of the tonsils is also characteristic. The sore throat that accompanies the disease is persistent and difficult to respond to antibiotic therapy. On the 4th day, petechiae appear at the border of the hard and soft palate. In the oral cavity, catarrhal herpetic or ulcerative necrotic stomatitis with petechial hemorrhages on the mucous membrane can be diagnosed.
There is even more relevant and useful information, including on diseases of the oral mucosa, in the section of our website Online courses, lessons and webinars on Periodontology .
