Closing the diastema without preparation
Machine translation
Original article is written in RU language (link to read it) .
After orthodontic dental treatment, patients are often faced with the need to close the diastema, which occurs due to microdentia. Treatment may include direct restorations using modern composite resins or indirect restorations using composite materials, glass ceramics, and new hybrid materials.
Ceramic veneers: all popular protocols [ in one place ] – an online course that contains all the clinical and laboratory protocols for working with ceramic veneers.
Currently, indirect restoration methods can be used in various clinical cases. In most cases, preparation for prosthetics is not necessary if the teeth are small. However, what you need to pay attention to is the axis of insertion, which in most cases is buccal.
Treatment methods without preparing tooth tissue have significant advantages: preservation of natural enamel, management and control of the gingival contour, as well as reduction of working time.
This article discusses modern approaches to correcting microdentia and closing the gap between the upper lateral incisors.
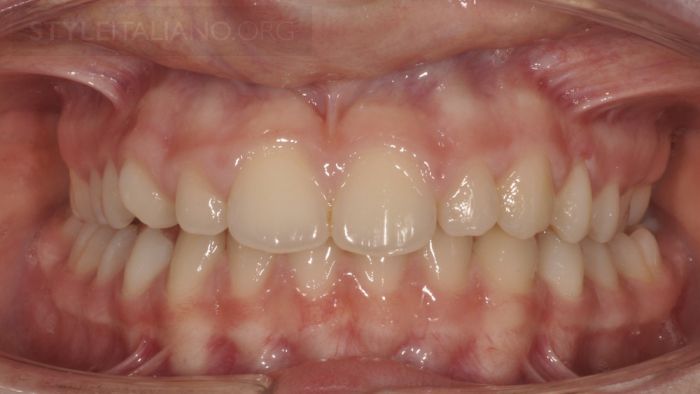
Drawing. 1. Frontal view, initial situation.
Drawing. 2. Patient RG has microdentia of teeth 1.2 and 2.2, lateral bite on the right.
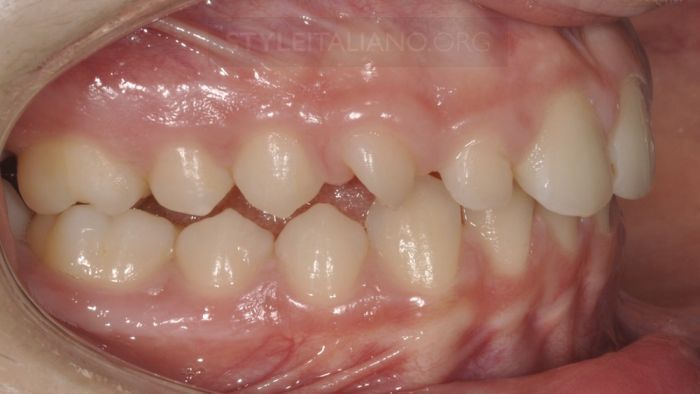
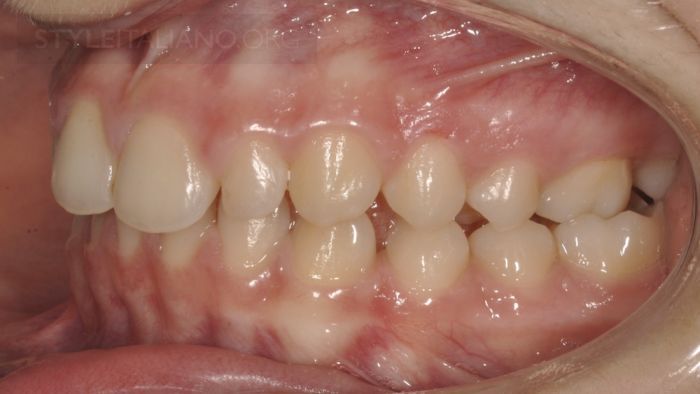
Drawing. 3. Rotation of tooth 1.3 is associated with noticeable gaps between teeth 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 and a straight open bite.
Drawing. 4. The patient turned to the orthodontist to solve the listed problems.
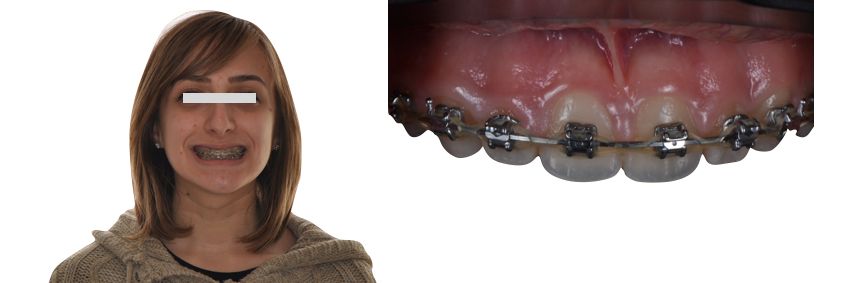
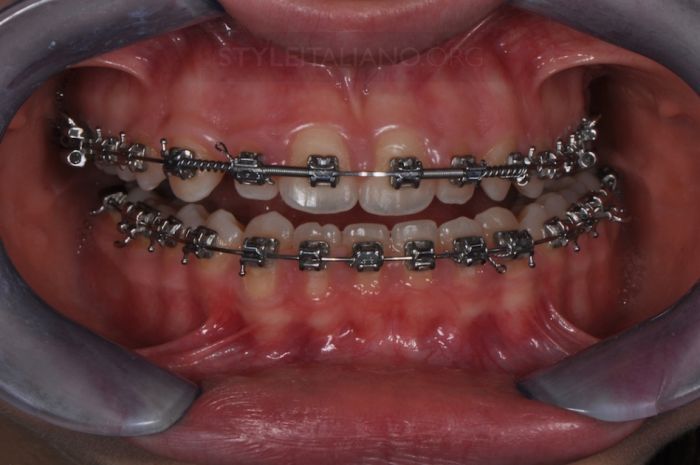
Drawing. 5. To facilitate the correct closure of the teeth, which will be ensured by the orthodontist, and to create ideal conditions for the final restoration, temporary composite crowns are made for teeth 1.2 and 2.2 without the use of adhesive technology, which will facilitate their removal after orthodontic treatment.
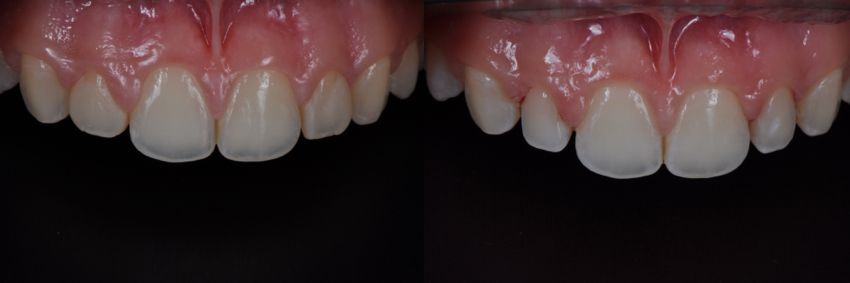
Drawing. 6. View after applying temporary crowns (photo on the left), then after removing them after orthodontic treatment.
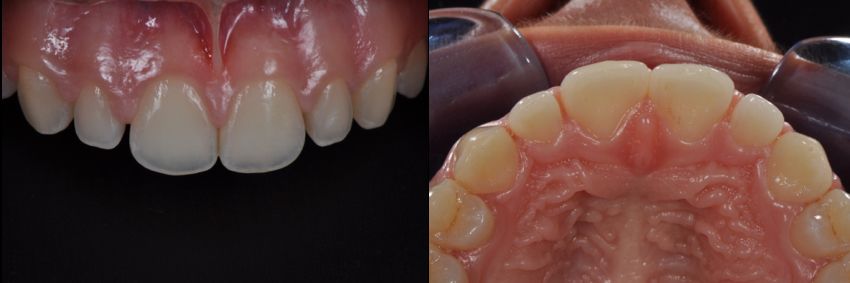
Drawing. 7. Trema between the lateral incisors after orthodontic treatment (frontal view on the left, occlusal view on the right).
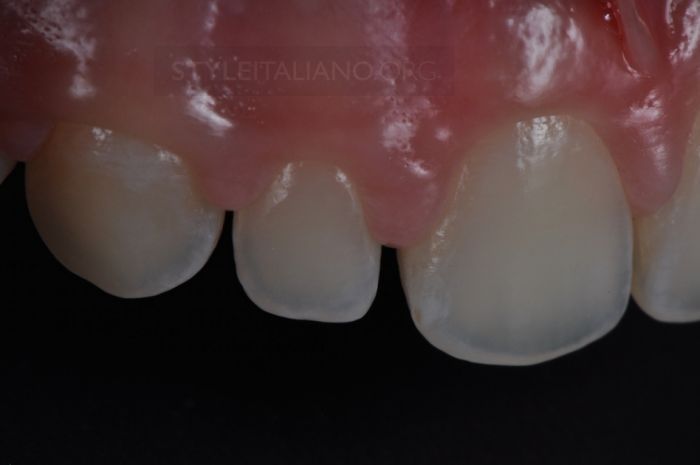
Drawing. 8. Enlarged view.
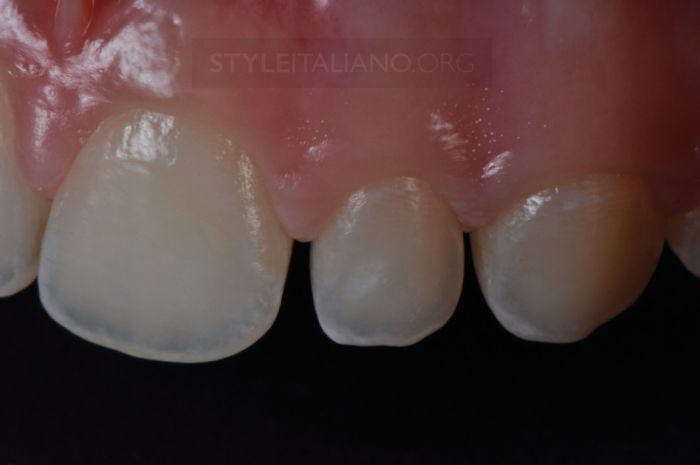
Drawing. 9. Left view, enlarged view.
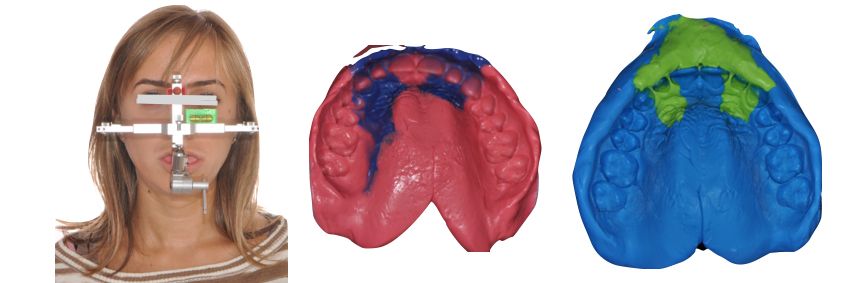
Drawing. 10. Applying a facebow and making an impression for the subsequent production of two veneers on teeth 1.2 and 2.2.
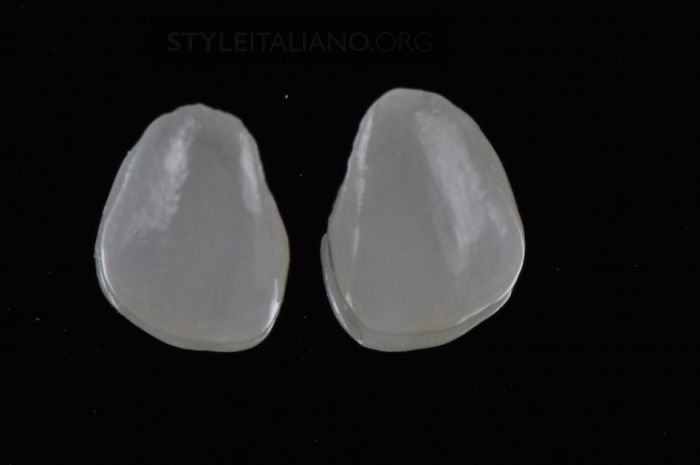
Drawing. 11. Lithium disilicate veneers, pressed and painted.
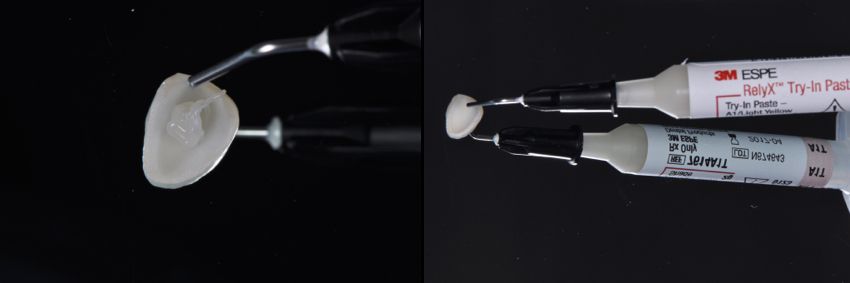
Drawing. 12. Color assessment is carried out using special test pastes. This material is applied to the inner surface of the veneer, simulating the material that will be used for fixation.
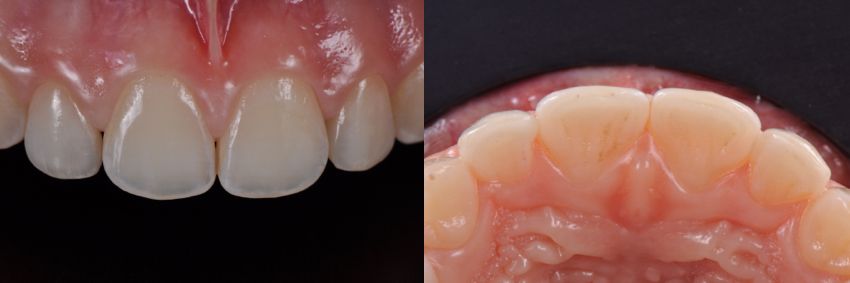
Drawing. 13. Trying on veneers, frontal view on the left, occlusal view on the right. Observe complete closure of the trema and optimal aesthetic results.
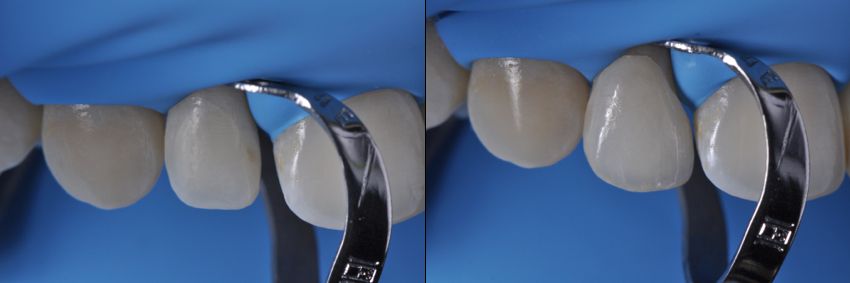
Drawing. 14. For insulation we use Rubber dam. Final fitting of the veneers, then cementing them one by one.
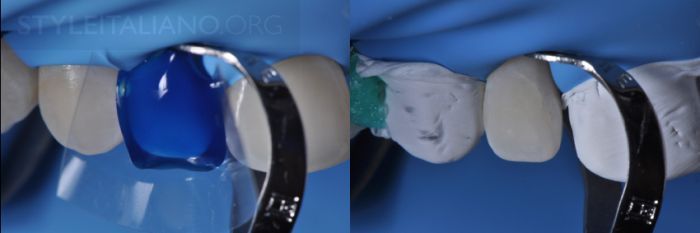
Drawing. 15. Detailed details of the procedure for etching and protecting adjacent teeth from contamination with a transparent matrix and then Teflon. To properly perform the adhesive technique, it is recommended to sandblast with 50 micron aluminum oxide and continue etching for 60 seconds on the buccal surface.

Drawing. 16. Use of the latest generation universal adhesive. Its consistency is quite viscous, so it polymerizes more slowly, but simultaneously with the cement chosen for fixation. This avoids unnecessary areas of thickening in the creation of restorations.

Drawing. 17. Etch the inner surface of the veneer using hydrofluoric acid for 20 seconds. After etching and washing, we use the same universal adhesive and apply without polymerization.
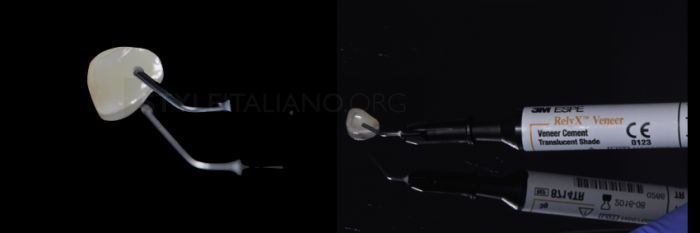
Drawing. 18. Apply the selected cement to the inner surface of the veneer.
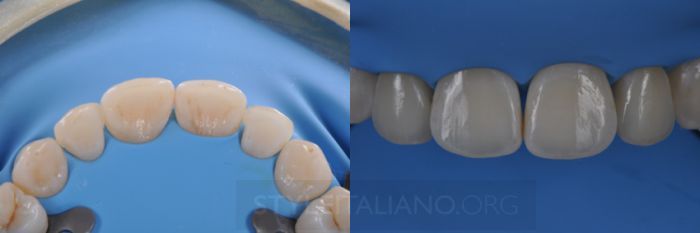
Drawing. 19. After cementation, excess removal and finishing.
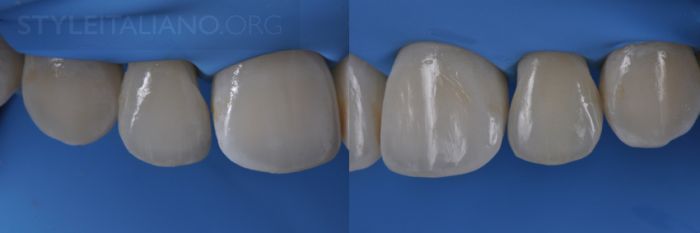
Drawing. 20. After final restoration.
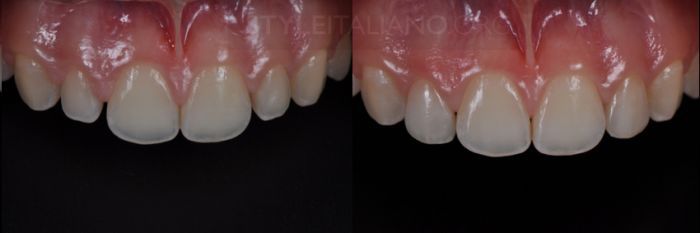
Drawing. 21. View before and after.

Drawing. 22. The patient’s smile after treatment.
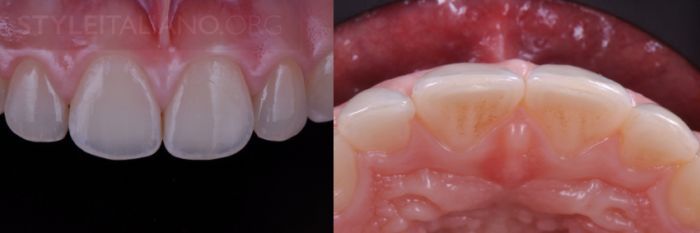
Drawing. 23. 1 month after the restoration.
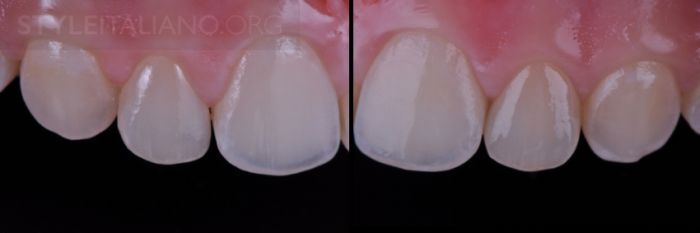
Drawing. 24. Closing the thread.
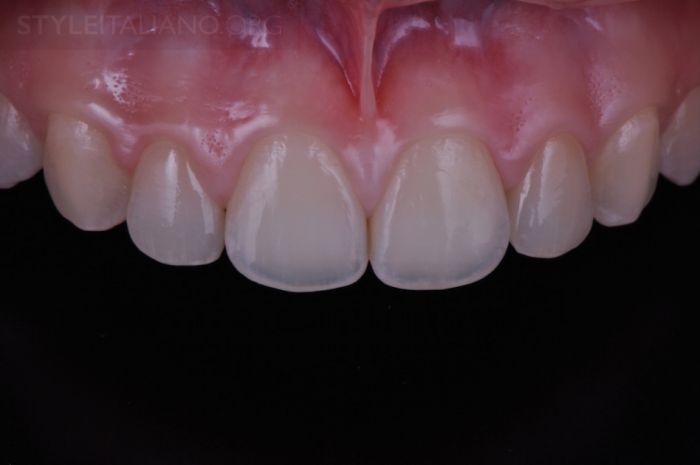
Drawing. 25. 1 year after treatment. A very good result was achieved.
Conclusion
Treatment methods that preserve natural tissue are increasingly being developed. Preservation of the tooth’s own tissues and its individual structures should be one of the main goals in planning the treatment of aesthetic and functional defects.
About the features of micropreparation of the interproximal zone for ceramic veneers at the webinar Ceramic veneers. Features of preparation .
http://www.styleitaliano.org/
