Errors in endodontic treatment during the tooth cavity opening stage
Machine translation
Original article is written in RU language (link to read it) .
Endodontics is a branch of dentistry where the doctor is required to perform precision work, most manipulations are carried out in conditions inaccessible to the eye, and the specialist needs knowledge, manual skills, and tactile sensations.
Treatment techniques for perforations in the webinar Root Perforations - Diagnosis and Treatment.
Mistakes and complications occur at any stage of endodontic treatment. The reasons are varied, but the most common can be identified:
- low qualification of the specialist;
- non-compliance with work techniques;
- lack of technical equipment, tools;
- limited assortment of medications and materials.
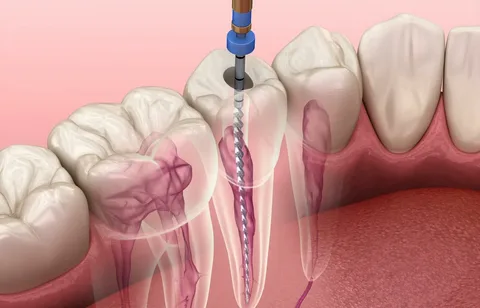
Figure 1. Creating access for endodontic treatment.
In this article, we will discuss the mistakes that are most often made in the initial, preparatory stage of endodontic treatment.
Mistakes made during the preparation of the carious cavity
All mistakes at this stage are related to two main reasons:
- softened infected dentin is not completely removed, remnants are left on the walls of the cavity;
- too much damage to healthy tissues during preparation.
If the softened infected dentin is not completely excised during endodontic procedures, infection of the root canal and subsequently the tooth's periodontium may occur. Even the visibility of the cavity is hindered, which leads to the inability to detect the canal orifices, increasing the risk of missing an additional canal.
How to avoid this mistake
After preparation, it is necessary to dry the carious cavity and thoroughly assess the quality of the preparation.
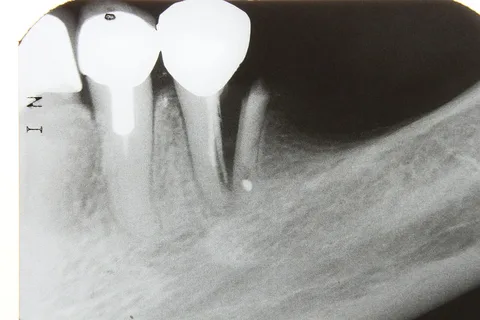
Figure 2. Tooth fracture due to excessive preparation.
Error correction: in the case of retaining softened dentin on the cavity walls, necroectomy should be continued.
Active excision of intact tissues during the creation of endodontic access will lead to weakening and fracture of the tooth wall. This error is due to a lack of knowledge of the anatomical structure of the tooth cavity, or an incorrect choice of the tip at this stage.
Prevention
It is important to perform only justified dissection, know and adhere to classic access options to the canal orifices, but not forget about the individual features of the tooth crown configuration, about the inclinations of the teeth. The necroectomy stage is carried out with a micromotor handpiece, visual control is necessary.
Error correction: thinned walls are covered with composite materials immediately upon detection, or after the completion of endodontic treatment, the patient is recommended to undergo orthopedic treatment.
Errors typical for the biological method of treating pulpitis
Thermal or mechanical irritation of the pulp. Occurs during dissection without cooling, using an uncentered handpiece. This leads to chronic pulpitis or periodontitis.
Prevention: studying the topography of the teeth, strictly following the dissection technique.
Error elimination: traditional endodontic treatment with pulp extirpation.
Opening the tooth cavity. Associated with the doctor's desire to thoroughly remove softened tissues from the bottom of the carious cavity. This leads to trauma and infection of the tooth cavity.
Prevention: studying the topography of teeth, strict adherence to the protocol of asepsis and antisepsis.
Correction of the error: use of a therapeutic liner, if this does not help, pulp extirpation must be performed.
Errors occurring during the preparation of the tooth cavity
All errors at this stage can be divided into the following groups:
- Excessive tissue excision when creating endodontic access.
- Opening is limited to the "horn" of the pulp.
- Perforation of the tooth wall.
- Incomplete removal of the pulp chamber vault, preservation of overhanging edges.
- Distortion of the configuration of the walls of the pulp chamber and the floor of the tooth cavity.
- Opening the floor.
- Perforation at the level of the tooth root neck.
Excessive tissue excision when creating endodontic access
This occurs as a result of the doctor's desire to create the best visibility of the cavity to facilitate the search for canal orifices, causes excessive opening of the tooth cavity, leads to weakening of the tooth crown in the future, and may contribute to the formation of a ledge above the canal orifice.
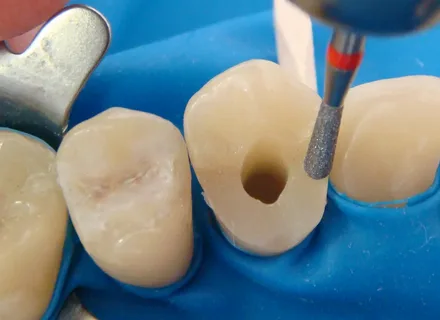
Figure 3. Removal of all overhanging walls.
How to prevent: During dissection, it is important to ensure that the walls of the cavity smoothly transition into the walls of the pulp chamber.
Error correction: restoration of weakened crown walls.
Opening limited by the "horn" of the pulp
During the trepanation of the remaining crown, perforation of the cavity vault, and the opening of the "horn" of the pulp, are often mistaken for the opening of the canal orifice. This error is typical for inexperienced doctors and is associated with caution and lack of knowledge of the topography of the pulp chamber, difficulties in distinguishing the bottom of the pulp chamber from the bottom of the carious cavity. As a result of this error, there will be difficulties with access to the canals, the tooth cavity will not be cleared of necrotic masses, increasing the load on the endodontic instruments. This will significantly complicate the search for canal orifices, and even more so their obturation, which cannot be performed qualitatively. This error is considered the most severe at this stage of treatment.
How to avoid: sufficient exposure of the carious cavity, studying the features of the pulp chamber topography, radiological control of all stages.
Treatment: completely remove the roof of the tooth cavity, ensure adequate access to the canals.
Tooth wall perforation
Caused by a lack of knowledge of the topographical nuances of the tooth cavity, excessive opening of the canal orifices. Factors that can lead to this complication:
- lateral narrowing of the crown;
- worn walls in the cervical region of the tooth;
- the bottom of the tooth cavity is relatively deep;
- limited visibility.
Prevention involves careful preparation, and in case of complications, restoration of the defect with filling material is used.
Incomplete removal of the pulp chamber roof, preservation of overhanging edges
This error is the result of insufficient preparation of the tooth cavity. Quality endodontic treatment is impossible, access to the canals is hindered; necrotic masses remain under the overhanging edges; endodontic instruments are subjected to increased load.
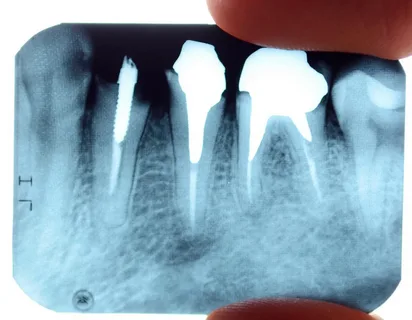
Figure 4. Development of complications due to errors in endodontic treatment.
Prevention
Following recommendations for creating an access cavity:
- for posterior teeth – from the occlusal surface;
- for incisors and canines – from the oral surface.
Excision of overhanging edges, formation of a Class I cavity. Monitoring is carried out visually and by probing.
Prevention: strict adherence to the rules for creating endodontic access.
Violation of the configuration of the pulp chamber walls and the floor of the tooth cavity
Caused by a lack of knowledge of the topography of the pulp chamber or careless preparation in the area of the tooth cavity. Accompanied by perforations of the pulp chamber walls, complicating the detection of canal orifices. A typical complication is the excision of the protruding "dome" in the area of the floor of the tooth cavity.
Precautions: strict adherence to the treatment protocol. The tooth cavity is prepared using a micromotor handpiece. It is fundamentally important to have an understanding of the topography of the pulp chamber.
Remediation of consequences: careful search for orifices, mechanical and medicinal treatment of canals, mandatory radiological control.
Opening the floor of the tooth cavity
Caused by excessive force during the preparation of the floor of the pulp chamber, often due to mistaking the floor of the tooth cavity for the floor of the carious cavity. Factors that can lead to this mistake include:
- the height of the crown is reduced due to significant wear of the occlusal surface,
- increased deposition of reparative dentin, which is accompanied by changes in the volume and configuration of the tooth cavity.
This error significantly worsens the treatment prognosis; it leads to additional material and time expenses; in some cases, tooth extraction is required. Possible perforation is indicated by pronounced bleeding in the area of the pulp chamber floor. Radiological control with the introduction of a file helps to confirm the presence of perforation.
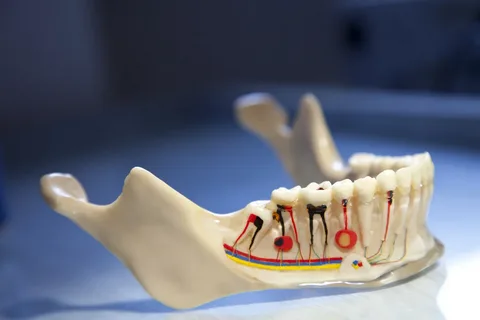
Figure 5. Features of the tooth cavity topography.
Precautionary measures: careful preparation, knowledge of the location of the tooth cavity.
Treatment: closure of the perforation, using materials:
- MTA (mineral trioxide aggregate);
- ProRoot (Dentsply);
- Trioxident (VladMiVa).
Perforation at the level of the tooth root neck
Occurs when working with incisors and canines, often due to the tooth's inclination. Worsens the prognosis of endodontic treatment.
Prevention: a precise understanding of the variations in tooth cavity placement, careful preparation.
Treatment: closure of the perforation using glass ionomer cement.
About the prevention of iatrogenic defects in the webinar Solving Endodontic Mistakes: Predictable MTA Practice.
