Modern concept of endodontic treatment
Machine translation
Original article is written in RU language (link to read it) , IT language (link to read it) .
Endodontics is one of the branches of dentistry that studies the structure and functioning of the pulp and periapical tissues. Her research is focused on elucidating the physiological norms and pathological processes in the pulp and periodontal tissues and their prevention.
The modern concept of endodontic treatment involves the elimination of infection from the root canal, a therapeutic effect on periapical lesions in order to restore a single periodontal barrier, and the prevention of bacterial invasion.
To achieve results, you must consistently perform the following tasks:
Thoroughly clean the root canal of pulp residues, bacterial agents and their metabolic products, and disinfect the cleaned canal.
Perform endodontic preparation of the canal, ensuring complete mechanical removal of infected dentin.
The prepared root canal is subject to three-dimensional obturation to restore a biological barrier that will prevent re-infection.
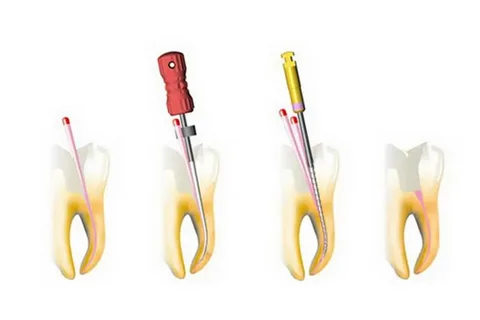
Figure 1. Stages of root canal filling.
Endodontic treatment is aimed at preserving the tooth for a long period of time as an integral part of the masticatory apparatus, ensuring the health of periodontal tissues and preventing infection and sensitization of the body.
The following stages of endodontic treatment can be distinguished:
A set of preparatory measures for endodontic treatment.
Instrumental and antiseptic treatment of canals.
Obturation of canals.
Postendodontic restoration.
Preparatory stage of endodontic treatment
Planning is an important and integral stage of endodontic treatment, requiring the manifestation of medical thinking from the dentist.
Planning can be divided into its component parts:
clinical examination,
diagnostic procedures,
informing the patient about upcoming treatment,
preparation of tools,
choice of anesthesia technique and treatment method.
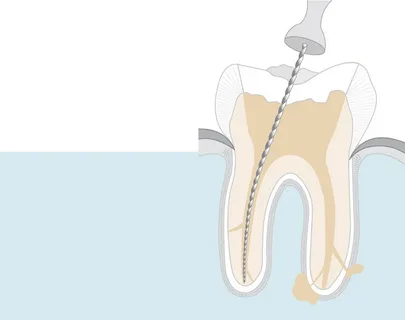
Figure 2. Root canal passage.
The above steps can be completed in one or two visits. It is preferable to perform pulpectomy of an intact tooth immediately, as this will eliminate pain between visits. If endodontic treatment of a multi-rooted tooth is contemplated, it is most often performed in two visits.
The preparatory stage includes the following activities:
Diagnostics.
Anesthesia.
Isolation of the tooth to guarantee safety and asepsis of manipulations is carried out by applying a rubber dam.
Providing access to the root canal system.
Diagnostics
Before starting endodontic treatment, it is necessary to ensure the accuracy of the diagnosis. Diagnosis is impossible without the use of additional research methods:
radiography;
thermal test or freetest;
electroodontodiagnostics.

Figure 3. Endodontic instrumentation.
X-ray diagnostics is an additional method, but this study is mandatory for endodontic treatment. The endodontic treatment protocol involves taking several radiographs:
diagnostic;
to clarify the working length of the roots;
to assess the quality of root canal obturation;
to control the quality of long-term treatment results.
These radiographs are mandatory, but sometimes it is also necessary to additionally perform a radiological assessment of the quality of installation of the main pin.
Dental computed tomography is a promising X-ray examination technique that has undeniable advantages in the process of planning endodontic treatment:
Good information content of the image (allows you to evaluate the number of canals, their configuration, clarify the projection of the apical foramen, the presence of deltoid branches, the presence of inflammatory lesions in the apex area, the quality of obturation of the root canals).
Allows you to measure anatomical structures with high accuracy.
Helps to examine in detail each component of the dental system on any section.
However, this diagnostic procedure also has some disadvantages; here we can note the rather high cost of dental computed tomography and a relatively large radiation dose.
Figure 4. Endodontic treatment of the tooth.
Assessing tooth sensitivity in response to electrical or thermal stimuli helps determine the condition and vitality of the pulp. It is important to note that the differential diagnosis of a healthy pulp and any of its lesions, both reversible and irreversible, using a single test is significantly difficult due to the fact that intact areas of nervous tissue can be preserved even among severe necrosis of surrounding tissues.
Vitality tests get their name because they can help determine the vitality of the pulp. The most informative of them is the cold test or freeze test. To carry it out, you will need additional components: frigen, chloroethyl, ice cubes. According to studies, application of cold for 4 seconds reduces the temperature of the tooth to 25–30 °C, which promotes a pain response. Moreover, the pulp temperature decreases by only 0.2 °C.
The temperature of ice cubes is approximately 0 °C, while the temperature of frigen, which is available in the form of a spray and applied to the cervical area of the tooth with an applicator or cotton ball, is –40 °C.
You can evaluate the tooth’s reaction to a high-temperature irritant by using heated gutta-percha (not pins, but sticks with a high melting point) or heated wax.
It is worth noting that the method of assessing the sensitivity of a tooth to cold using a directed stream of air is not of informative value. When conducting temperature tests, it is important to remember the most sensitive area of the tooth crown, which is the neck of the tooth. Here there is a minimum thickness of hard tissues, a minimum distance to the pulp chamber, therefore the probability of an objective result of exposure to a temperature stimulus on the pulp is maximum.
Determining the electrical excitability of the pulp, this technique is called electroodontodiagnostics or EDI, is based on the conductivity of hard tissues. The device reproduces voltage pulses that are tuned to the resistance of the hard tissues of the tooth. Electroodontodiagnosis allows you to reliably determine the vitality of a tooth. But the probability of making a differential diagnosis of different forms of pulpitis using this technique is extremely small. Taking into account the diagnosis, the general condition of the patient and material equipment, the appropriate tactics of endodontic treatment are selected.
Anesthesia
Endodontic procedures require anesthesia.
Today, most dentists prefer endodontic treatment under adequate anesthesia rather than devitalizing drugs that have mutagenic and cytotoxic characteristics. In this regard, local anesthetics have found wide use in endodontics.
An absolute contraindication for the use of local anesthetics is allergies.
Isolation of the tooth to ensure asepsis
A rubber dam is a classic device used to isolate the working area during endodontic treatment.
Advantages of using rubber dam:
Allows you to isolate the tooth from saliva and moist exhaled air.
Allows you to isolate the tooth from aggressive bacterial flora of the oral cavity, implementing the principles of asepsis and antiseptics in practice.
Allows you to protect the working area from contact with the patient’s lips and tongue.
Allows you to protect the patient from direct contact with the medications used.
Prevents the effects of aggressive medications on the mucous membrane.
Prevents the possibility of accidental aspiration of small endoinstruments, guaranteeing safety for both the doctor and the patient.

Figure 5. Rubber dam in endodontics.
During the process, high-quality lighting and the use of increasing the working field are very important. The modern concept of endodontic treatment involves the use of an endodontic microscope or binocular loupes.
Providing endodontic access
The main condition for the formation of endodontic access is the excision of tissues that prevent direct access to the mouths of the canals.
Providing endodontic access requires the following steps:
Removal of old restorations, carious decay.
Opening the tooth cavity.
Excision of overhanging edges, opening of the cavity.
Finding the mouths of the canals.
Providing straight-line access.
Modern trends and technologies in endodontics from leading and recognized experts in the online course Endodontics today: expert protocols and new perspectives .
