Ways to Remedy Enamel Demineralization
Machine translation
Original article is written in RU language (link to read it) .
Focal demineralization is the process of primary destruction of tooth enamel at the initial stage of the carious process. If treatment is started at this stage, it is possible to avoid surface destruction and the spread of the process beyond the enamel and dentin—into the pulp and periodontium.
About the possibilities of remineralization of the remaining carious dentin in the webinar Biomimetic restoration of severely damaged molars.
Tooth enamel is composed of mineral substances, which are constantly renewed, maintaining the beauty and hardness of the teeth. In the case of demineralization, the mineral components of the tooth enamel disappear, which negatively affects its condition, weakening the teeth and causing them to rapidly deteriorate. Extensive carious defects appear on their surface, and then the pulp becomes inflamed.
If a patient is found to have focal demineralization of enamel, an important step is to strictly follow oral hygiene rules, with the main goal being to prevent the formation and prolonged retention of dental deposits in the area of the former demineralization spot.
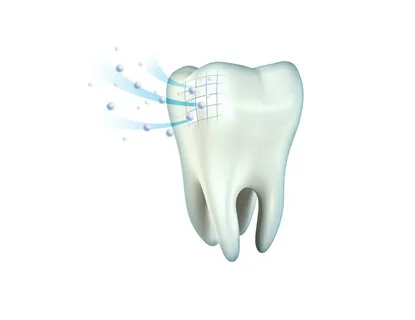
Figure 1. Ion exchange on the surface of enamel.
It is also extremely important to convince the patient to change their eating habits:
- reduce carbohydrate intake,
- eliminate carbohydrate intake between main meals.
Change of the spot color to black or brown indicates stabilization of the process. The course of pigmented spots in the vast majority of clinical cases is asymptomatic. The patient may complain about the presence of a cosmetic defect, they might suspect the presence of a cavity on their own, but there are no other complaints.
Causes of Pigmentation
The cause of pigmentation in carious spots has long been established and proven. Enamel and dentin tissues are capable of accumulating tyrosine, which subsequently transforms into the pigment melanin. This process is observed under the outer undamaged layer of enamel. It has been established that in the middle of such a spot, microhardness gradually decreases and permeability increases, especially for radioactive calcium.
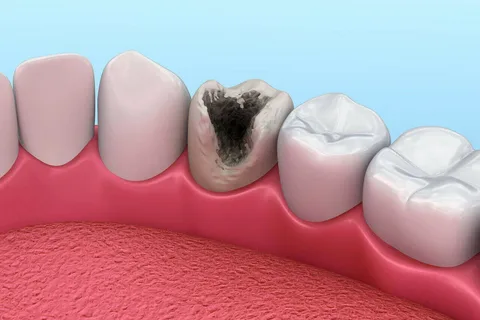
Figure 2. Pigmentation of a demineralization area.
Laboratory and clinical studies have demonstrated the low effectiveness of remineralizing therapy in diagnosing such changes. These lesions exist on the tooth surface for a long time and eventually turn into carious cavities, and after several years, the enamel-dentin connection is disrupted.
Methods of Elimination
If the focus of pigmentation on the tooth enamel surface is small, dynamic observation is recommended. If the area of pigmentation is extensive, one can immediately proceed to preparation and subsequent restoration, without waiting for the formation of a carious cavity. In most clinical situations, it is advisable to grind off the pigmented fragment, followed by remineralizing therapy.
Deep Fluoridation
The technique of deep fluoridation of tooth tissues was first introduced in Germany by A.Knappowost. It involves the sequential use of several agents that are applied to the enamel, dentin, or cementum, where in their presence, calcium fluoride crystals are formed. These crystals ensure the sealing of dentinal tubules and pores in the enamel.
The set is represented by two drugs:
- fluoride silicate,
- highly dispersed mixture of calcium hydroxide-copper.
As a result of using the mixture of these drugs, calcium fluoride is formed deep within the dentinal tubules and enamel pores, which results in a high concentration of fluoride ions and creates the conditions for the formation of apatites inside the tubules, ensuring an additional desensitizing effect.
Enamel Infiltration
This treatment method was proposed by H.Meyer-Lucker and S.Pariset al., it is
based on halting the carious process thanks to sealing the pores on the enamel surface, which remain gaping after the acids have entered and dissolved minerals have been washed out.
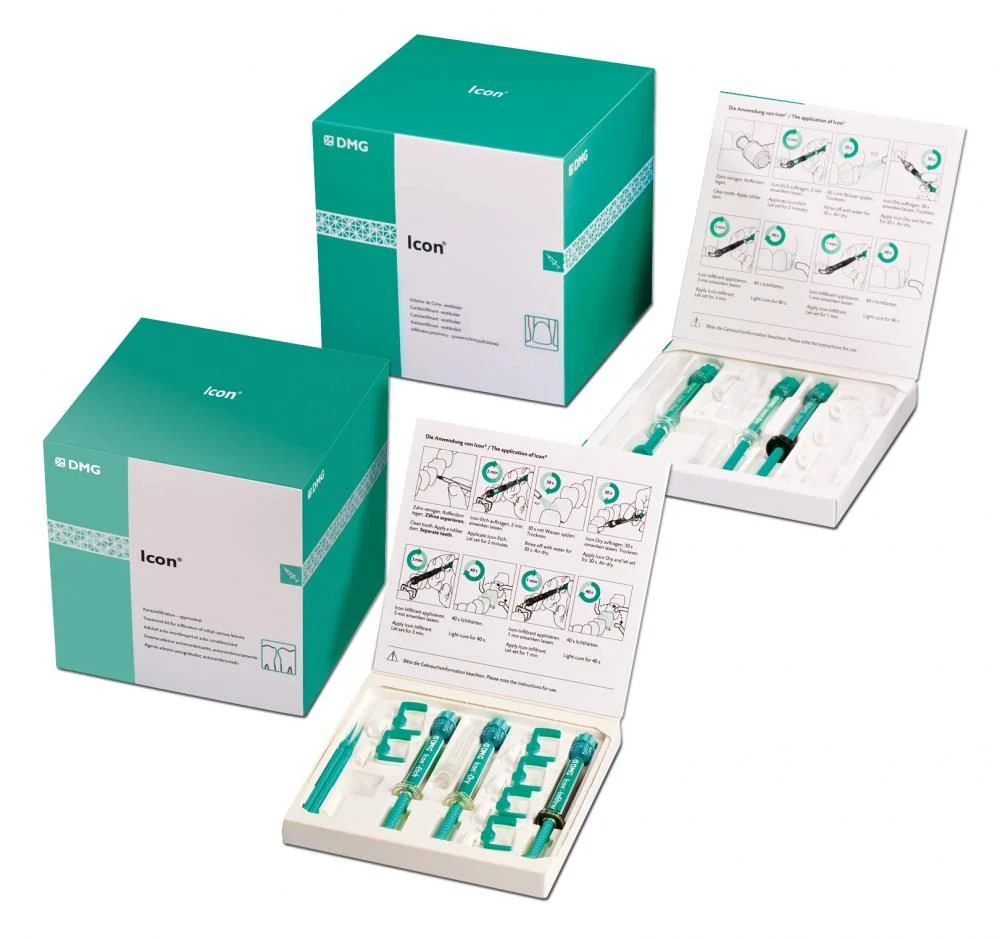
Figure 3. "Icon" Set.
Currently, the company "DMG" produces the "Icon" set, which is available in two versions: Vestibular and Aproximal.
The set includes the following main components:
- Icon Etch – this is an etching agent, it has a gel consistency, presented by 15% hydrochloric acid;
- Icon Dry – this is an ethanol-containing conditioner;
- Icon-Infiltrant – this is an infiltrant.
Using GC Tooth Mousse Cream
The remineralizing therapy using "Tooth Mousse" cream from GC is due to the content of the Recaldent component in this cream, which is represented by casein phosphopeptide, obtained from casein protein, containing "attached" calcium ions and phosphate ions on its surface.
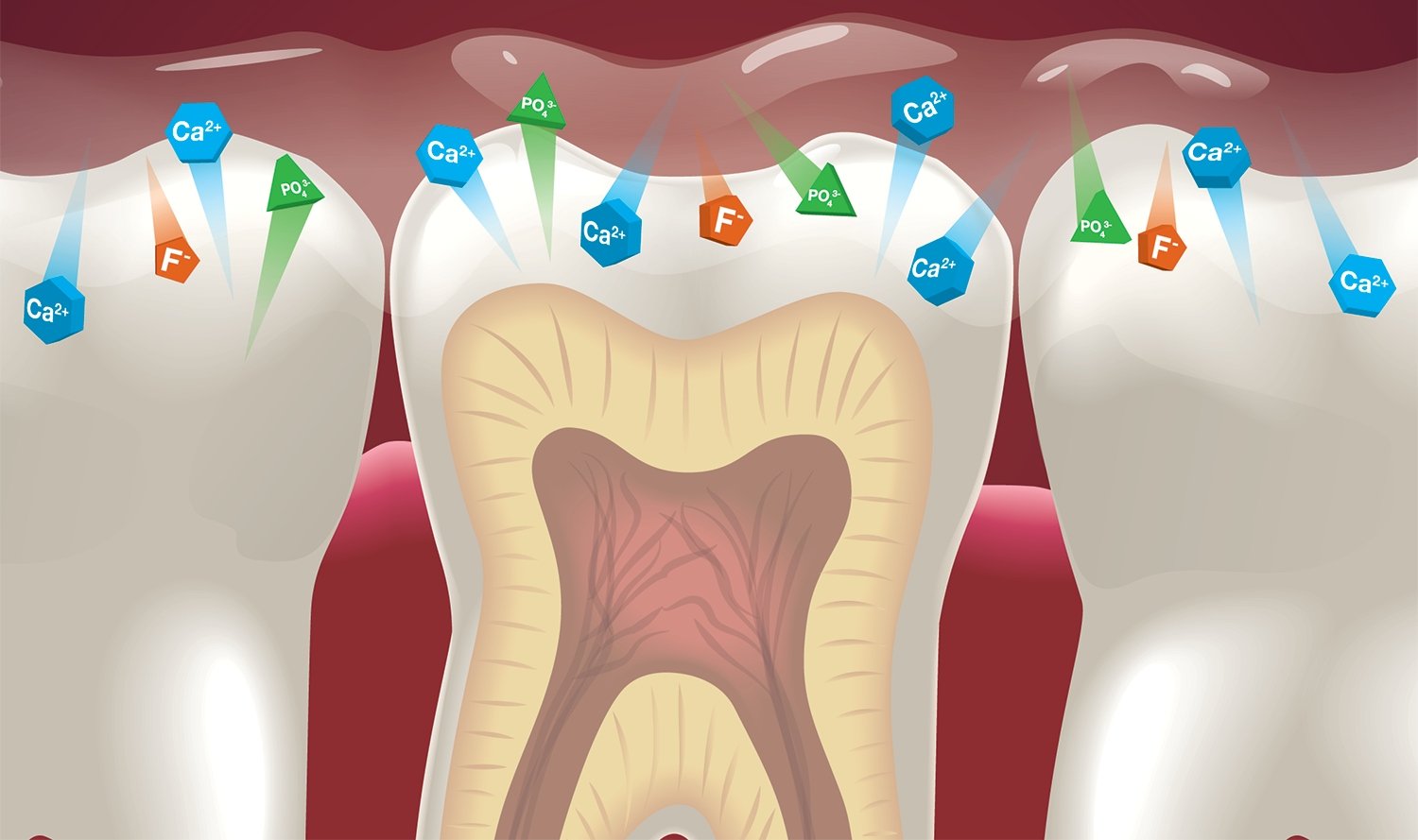
Figure 4. The principle of remineralization.
Casein phosphopeptide allows the retention of phosphate ions and calcium in a non-crystalline amorphous state and provides excellent adhesion of the product to tooth tissues, biological film, pellicle. The complex is easily absorbed on the enamel surface and begins to gradually release phosphate ions and calcium ions into the peri-tooth space, while the remaining portion of amorphous phosphate and calcium, still held by casein, maintains the activity of these ions, ensuring the maintenance of the gradient of calcium and phosphate ion concentrations, which is important for their transport into the subsurface area of the demineralization site.
Ozone Therapy
At the University of Belfast, a group of researchers led by Professor Edward Lynch developed a unique method for treating early forms of caries – with ozone. During laboratory experiments, it was found that under the influence of ozone, up to 99.9% of microorganisms die within 20 seconds in the carious cavity. The result of these studies was the creation of the HealOzone device. This is an electrical discharge ozone generator, which allows creating the necessary concentration of gas in the chamber that contacts the tooth surface. Gas circulation occurs at a rate of three hundred cycles per minute. Air is taken from the surrounding environment, sucked into the device, and then dried.
When the flow meter under the silicone cap of the tip registers a vacuum, the ozone generator is activated. As a result of a high-frequency electrical discharge, oxygen is converted into ozone. A controlled volume of ozone is delivered to the tip and reaches the surface of the tooth damaged by caries. Then, in a closed cycle, the ozone returns to the tip.
The hydrophobic filter prevents moisture from entering the ozone neutralizer. Ozone is converted back into oxygen. Thanks to the operation of the vacuum pump, a continuous flow of air is ensured, and oxygen is evacuated to the external environment.
Ozone Therapy Sequence
- The tooth surface is thoroughly cleaned using a powder jet device. The presence of initial signs of caries is confirmed during an examination with the DIAGNOdent device.
- The use of the HealOzone device eliminates a significant number of microorganisms.
- Remineralizing therapy is carried out using a special solution.
- Subsequently, the patient continues treatment at home, and remineralization of tooth tissues is stimulated by using a special HealOzone kit for a month.
- A follow-up visit to the dentist to assess the remineralization process and the overall condition of the oral cavity.
If destructive damage to hard tissues is diagnosed, gentle preparation is performed using a powder jet device, the cavity is treated with HealOzone, then the tooth is filled with materials that promote additional mineralization.
If there are indications, aesthetic restoration with composite materials is performed. It is important to consider the factor that after the elimination of microorganisms in the carious cavity and before the start of filling, a period of 1 to 1.5 months should pass, during which remineralization takes place.
Figure 5. HealOzone device.
Clinical signs of caries removal are confirmed by the following manipulations:
- upon probing, a significant hardening of the tissues previously softened by caries is felt;
- chalky spots are absent on the dried tooth surface;
- the indicators recorded using the DIAGNOdent device are reduced;
- demineralization, previously noticeable on the radiographic image, decreases or is completely eliminated.
The characteristics of the course of carious enamel lesions, the level of equipment of the material and technical base of dentists leads to a shift from a passive principle of diagnosis and therapy towards active diagnosis and subsequent treatment of initial forms of the carious process.
Minimally invasive methods of treating surface caries are presented at the webinar Minimally Invasive Cosmetic Methods for Treating Enamel Defects.
